IMS service is stopped in my Samsung device. How can I fix this asap? Need help from any Android expert out there."
The above question was asked by an Android user recently on the help forum. Are you familiar with this situation? Or are you currently facing the same problem and looking for help like her? If so, then this is an article you should read. We will explain everything about the IMS service and how to fix it if there is an error related to it.
Samsung mobile devices come with an added UI layer on top of the default Android interface. This interface offers various basic applications that are used for messaging, browsing and system configuration. This user interface layer is known as IMS (short form of IP Multimedia Subsystem). Essentially, it is an architectural framework that provides multimedia services to consumers.
Overall, this service should run fairly smoothly without causing too many problems. However, recently there have been a large number of reports about the termination of the IMS service. The full message states: " Unfortunately, the IMS service has stopped ." This message appears out of nowhere, especially when they are trying to call or message someone.
What is the cause of the "IMS Service has stopped" error?
Method 1: Check for OS updates to fix "IMS Service has stopped"
Method 2: Check if there are any app updates
Method 3: Change Message Settings
Method 4: Start your device in Safe Mode to fix “IMS Service has stopped”
Method 5: Clear Cache to Fix “IMS Service Has Stopped”
Prerequisites for IMS implementation
Consolidation of operators and the ability to provide converged services
Competition between existing mobile operators remains very high, and active mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are taking place in the market. Companies providing different types of services (fixed and mobile telephony, mobile telephony and cable television, etc.) are often consolidated. IMS technology helps them combine all types of networks into one, implement a range of services that combines the capabilities of mobile and fixed communications based on one platform (convergent services) and provide operators with ARPU growth and increased revenue.
Threat from OTT services
Third-party providers of text, voice and video applications (OTT providers) are cannibalizing the traditional services of mobile operators (voice and SMS), which generate the bulk of the latter's revenue. With the advancement of technology (the transition to 4G), OTT providers are increasing the attractiveness of their services, for example, providing support for voice and high-definition (HD) video, which exacerbates the problem.
The need to reduce operator costs
An obvious trend in the global telecommunications market is the increase in capital expenditures of operators.
It is believed that IMS in the medium to long term will allow operators to reduce capital (CAPEX) and operating (OPEX) costs through the use of a single IP network and open IMS architecture. In addition, operators will be able to bring new services to market quickly and at low cost. However, at the initial stage of IMS implementation, operators will obviously have to increase their costs.
The emergence and development of LTE networks
The sharp increase in mobile data traffic consumption, intense competition and high demand for mobile broadband services requires the introduction of expensive LTE and LTE Advanced technologies. The development of 4G networks, in turn, encourages operators to implement IMS technology, as it makes it possible to implement voice services on LTE networks (VoLTE) and other services.
The essence of the problem
Often, when actively using a smartphone, you can observe a situation where the running program freezes and a warning is displayed: the application has stopped android, what should you do in this case?
This kind of problem is extremely unpleasant, as it can happen at any time both with applications built into the system and with third-party ones. As practice shows, such troubles are most often observed among owners of smartphones manufactured by Sony and Samsung, but they can also happen to other models of devices.
IMPORTANT! As a rule, such a problem is associated with an acute lack of resources in the system, causing one or more components to freeze during operation.
Among other things, the reasons for this unpleasant phenomenon include:
- The presence of bugs and errors in the current firmware of the device;
- System files have been modified or damaged;
- Incorrect device settings.
It is quite rare to see a situation where such negative manifestations are caused by an application conflict.
One-time passwords at a Sberbank ATM
Until February 2021, it was also possible to receive 20 one-time passwords at a Sberbank ATM, which were used to confirm the required Internet payment.
Receipt with a list of passwords
This technique turned out to be quite vulnerable. The fraudster picked up a discarded check with the specified 20 passwords, gained access to the user’s personal account, after which he was able to withdraw money from the user’s account 20 times.
Considering this sad practice, Sberbank decided to stop printing passwords using an ATM. Now payment confirmation is carried out exclusively via SMS to the client’s phone.
Is it possible to disable or delete
So, we already understood above - IMS Service is a system. And therefore it cannot be deleted. In theory, it’s impossible, but some users did delete it... and there didn’t seem to be any problems... Well, I found a message - deleting this thing is really dangerous:
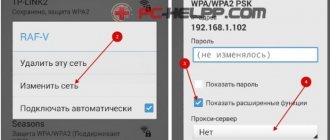
But as you can see, it turns out that you can disable/stop it.
Your phone most likely supports 3G, and therefore SIP telephony, but if you don’t use the latter, you can disable IMS:
- Dial the code *#*#4636#*#*
- A menu will appear - select Phone Information.
- Next, click something like mandatory IMS registration - disable it.
- After everything we do a reboot.
I read that the combination does not work on all phones, but it’s worth a try. Alas, I can’t check it myself, my phone is not on Android at all)) And yet, some users write that disabling IMS did nothing, and some even began to use more battery... In short, I advise you to check it yourself.
If disabling is problematic or doesn’t help, then you can freeze it, as one person did:
It is best to freeze using Titanium Backup.
So be careful, because IMS Service can not only use up the battery, but also heat up the phone)) And high temperatures are the enemy of the phone! And the computer too...
So, here’s some more info - you can try to disable it using BK Package Disabler - this is a special program for disabling unwanted applications on Samsung phones... but the trick is that you don’t need root access. So if you have a Samsung, try it, especially since judging by this screenshot, you can actually disable IMS Service with this program:
What does having IMS Service on board your smartphone provide?
If after reading you have not yet lost the thread of the discussion (the topic of this article), but did not quite understand the true meaning of the text of the quotes, then I will give an explanation on my own (may IT people forgive me): IMS is a universal data transfer service in modern communication networks (2G+ , 3G, 3G+, 4G...), using standard IP technology.
In particular, in the description of the IMS standard, we are talking about a new method of transmitting voice (and video, and SMS with MMS) calls via the LTE network.
For the common man, this means the following: now all 2G (wooden) and 3G telephones for voice and SMS transmission use the GSM standard of 20 years ago. All the power of new generation networks is used so that the user can surf the Internet and swipe messages with videos from friends on WhatsApp. Although, logically, a standard dialer should by default have the functionality of WhatsApp, Viber, Skype and others, and SMS should allow the transfer of gigabyte attachments. But no.
In fact, having at our disposal a super-sophisticated digital PBX, we use an old analog disk device for communication.
In fact, it turns out that voice communications operate at a frequency of 900/1800 MHz, in the 2G standard, SMS - in the same place, video calls (EDGE and higher) and MMS (GPRS / EDGE is enough) using IP technologies (frequency 2400 MHz) .
It turns out – one device, but completely different implementations of the method of transmitting data for services familiar in everyday life.
The task of IMS is to correct this problem by transferring all communication services to the level of IP technology, but with the inherent qualities of telephone networks, combining all services into one with the functionality of each of them.
Without going into details, this communication modification will increase the network capacity several times.
In addition to capacity, new functionality is added. For example, the simultaneous use of all services together.
And, by the way, one of the new features is to notify the interlocutor of your location during a call.
This setting allows this service to easily turn GPS on and off without your knowledge if necessary.
And IMS has such a need:
- You have voice transmission enabled via VoLTE (a type of VoIP).
- You make an emergency call.
- You are set to notify your interlocutor about your location.
It turns out that it is not IMS that is to blame for turning on GPS, but a completely different application that uses this service for communication.
Interestingly, in the settings of the standard Samsung dialer there is no option to disable or disable notification of the interlocutor about the location.
Just in case, to be 100% sure that your coordinates will not be transmitted to anyone during a call, you need to disable permission for IMS to change system settings.
The same setting will prevent the service from automatically turning on GPS on your device.
If I'm wrong somewhere, correct me. But, at least for me, this measure gave some result - IMS Service disappeared from the list of recent applications that recently accessed GPS. And this is hardly a coincidence.
General definitions
There are two main ways to transfer an IMS voice call from an LTE network to a legacy network. The first method is to continue the IMS call on the UMTS network by performing a PS handover. In this case, during the preparation and implementation of handover, the parameters of the EPS bearer virtual connection (including QoS parameters) are mapped into the PDP Context parameters. The second method is to transfer a voice call from a packet-switched network in the EPS/IMS domain to a circuit-switched network (SRVCC). In this case, packet traffic is stored in the PS domain (for example, through PS handover).
SRVCC technology was originally defined in 3GPP Release 8. In subsequent releases, the capabilities of SRVCC were expanded to support functions such as transfer from IMS domain to CS domain of emergency calls, transfer of multiple calls (active and held), transfer of calls in the connection phase, transfer video call, call transfer from circuit switched domain to EPS/IMS domain.
Support for SRVCC requires upgrading the MSCS of the 2G/3G network to enhanced MSCS, upgrading the MME and eNodeB to support the corresponding procedures, introducing a new IMS network application server on the network - SCC AS (Service Centralization and Continuity, - a server for centralized functions and service continuation), on which must be signed by the user, as well as the new Sv interface between the MME and MSCS (in accordance with 3GPP TS 29.280). The network architecture of SRVCC is shown in the figure below.
Rice. 62:
The main tasks solved by network elements within the framework of the SRVCC procedure:
SRVCC enhanced MSCS:
- support for Sv interface to MME;
- preparation of resources on the target radio subsystem;
- notification to the opposing party about the domain change;
- MSC anchor function (MSCA) for inter-MSC handover.
SCC AS:
- session anchor function in the IMS domain to enable future session transfer to a circuit-switched domain;
- forwarding the call to a circuit-switched domain;
- selecting a domain for terminating an incoming call to a VoLTE subscriber;
- providing the ability to remove unsupported media from a session after the session is transferred to a circuit-switched domain.
MME:
- indication of eNodeB support for the SRVCC function for a particular session;
- determining the correct virtual connection (EPS bearer) to transfer the session to the circuit-switched domain;
- support for Sv interface to MME;
- request “enhanced MSC Server” via the Sv interface and transmission of the necessary information to ensure the procedure for transferring a session to a circuit-switched domain;
- performing the necessary procedures for transferring non-VoIP sessions to a circuit-switched domain, for example, through PS handover;
- suspending and deactivating virtual connections (EPS bearer) if necessary.
E-UTRAN eNodeB:
- dynamic generation of a specific list of neighboring cells with SRVCC support to enable user terminal measurements;
- determining the need to transfer a session to a circuit-switched domain;
- MME request to initiate session transfer to the circuit-switched domain via the S1 interface;
- request the MME to initiate a PS handover in addition to the SRVCC procedure.
To summarize everything written above
The IMS service, one way or another, can independently control the device, as it is written in the explanation for the function of making changes “for example, enable or disable bluetooth,” respectively, the same applies to geolocation. To get rid of such surprises, simply prohibit the service from changing system settings.
As for energy consumption, according to eyewitnesses (and our own), disabling forced IMS registration does not lead to any noticeable energy savings, and some comrades note an increase in consumption (fact!)
So, during normal operation of the service, there is no need to carry out any manipulations with it. In 99% of cases, manipulating it only worsens the operation of the device.
Warm hello everyone, so take a look:
IMS Service is a standard for data transmission in 2G+, 3G, 3G+, 4G and future networks, but using IP telephony. It is part of Android, that is, it is a system.
Guys, I’m certainly not very good at it, but I read on the forum that IMS Service is needed for VoLTE to work. What is VoLTE? In simple words - a faster standard for data transmission, including voice, everything is much faster and better than in 3G.
Just a minute. To avoid confusion, VoLTE operates on the basis of IMS Service.
Guys, sorry, let me answer briefly right away. IMS Service is a standard - yes, it is good, it is fast, it is cool. But so far all this in Russia is raw. For now, and I think GSM/3G will be relevant for a couple of years. So you can safely turn it off. Here is a comment that confirms that for now there is no particular point in IMS Service:
Maybe in five years things will be better... but for now... I would turn it off. Although, to be honest, I read that some operators seem to support it... but only in Moscow and St. Petersburg..
Here is even more detailed information about IMS:
It’s just that now data is transmitted in the same way as it was 20 years ago - using standard GSM. And the downside is that voice communications and SMS operate at a frequency of 900/1800 MHz, that is, in the 2G standard. Everything else is already at a higher frequency - 2400 MHz.
And the task of IMS Service is to take all this to a new level, or rather to the use of IP telephony. Among the notable advantages is that you will be able to use many services at the same time; for example, the option of notifying your interlocutor about your location will be available.
That is, the IMS Service application can transmit your coordinates to the interlocutor? Yes, this may not be to everyone's liking, so to disable it, you need to change the application permissions so that it cannot change system settings:
This setting will also prevent the service from automatically turning on GPS on your phone. Do you understand what needs to be done? You need to prevent this program from changing application settings. Here's one user already complaining:
Well, you can stop this application altogether.
Reasons for the error The device is not certified for Android
Starting in March 2021, Google began blocking access of uncertified devices (i.e., those phones and tablets that have not passed the necessary certification or do not meet some of Google's requirements) to Google Play services.
The error could have been encountered before on devices with custom firmware, but now the problem has become more widespread and not only on unofficial firmware, but also on simply Chinese devices, as well as in Android emulators.
In this way, Google is fighting the lack of certification on cheap Android devices (and to pass certification, they must meet Google's specific requirements).
Clear cache and application data
If you have not updated a program for a long time and then decide to update to a new version (several intermediate versions were skipped), then you may encounter an error. To solve the problem, go to settings, open the list of all installed applications, open the settings of the program you need and clear the cache and delete data. It is worth considering that after deleting the data, all your saves in the game or program settings will also be deleted. If this does not help, then try simply uninstalling the program and installing it again.
What you need to know about data protection in a bank using 3D-Secure
Security of online purchases is one of the most important tasks for banks and payment systems. The increase in the number of such purchases attracts many attackers who want to gain access to user data and then steal money from the bank accounts of such users. To prevent such scenarios, banks are actively using various technologies, one of which is the popular “3D-Secure” technology.
“3D-Secure” is a special XML protocol that supports the security of online payments using payment cards. Codification "3D" means the use of three independent domains (D):
- a bank serving a specific chain store;
- bank - issuer of the payment card;
- payment system domain (Visa, Master Card and others).
An important stage of client payment identification in 3D-Secure is entering a confirmation password on a secure page on the Internet. Such a password can only be obtained by phone via SMS, which significantly reduces the chances of an attacker to intercept and replace such a password. After entering the password, payment confirmation and payment for the selected product are carried out.
Using SMS with a password allows you to secure online purchases
story
- IMS is defined by an industry forum called 3G.IP, formed in 1999. 3G.IP developed the initial IMS architecture, which was matured into the 3rd Partnership Project (3GPP), as part of its work to standardize 3G mobile phone systems for UMTS networks. It first appeared in version 5 (the evolution from 2G to 3G networks), when multimedia-based SIP was added. Support for legacy GSM and GPRS was also provided by the network.
- 3GPP2 (another organization from 3GPP) based on their CDMA2000 Multimedia Domain (MMD) on the 3GPP IMS, adding support for CDMA2000.
- 3GPP release 6 added internetworking with WLAN, interoperability between IMS using different IP connectivity networks, group identity routing, multiple registration and forked presence, speech recognition and voice service functions (PTTAMI).
- 3GPP Release 7 adds support for fixed networks by working together with TISPAN release R1.1, AGCF (Access Gateway Control Function) and PES (PSTN Emulation Service) are introduced into the wireline network for the purpose of inheriting services that can be provided in the public telephone network use. The AGCF operates as a bridge linking the IMS network and the MeGaCo/H.248 network. Megaco / H.248 network provides the ability to connect terminals of old legacy networks to new generation networks based on IP networks. The AGCF acts as a SIP user agent towards the IMS and performs the role of a P-CSCF. SIP user agent functionality is included in the AGCF, not on the client device but on the network itself. Continuity Also added are voice call between circuit switched and packet switched domain (VCC), fixed broadband connection to IMS, interworking with non-IMS networks, policy and charge control (PCC), emergency sessions.
- 3GPP release 8 added support for LTE/SAE, multimedia session continuity, enhanced emergency sessions and IMS centralized services.
- 3GPP release 9 added support for IMS emergency calls over GPRS and EPS, enhancements to multimedia telephony, IMS media security plane, enhancements to service centralization and continuity.
- 3GPP Release 10 added support for inter-device transmission, Single Radio Voice Call Continuity (SRVCC) enhancements, PIMA emergency session enhancements.
- 3GPP Release 11 added USSD service simulation, network provided location information to IMS, SMS send and delivery without MSISDN to IMS, and congestion control.
Configuring SIP agent of the IMS (Beltelecom) network on the CISCO router
Currently in Belarus, the telecommunications operator Beltelecom is intensively introducing telephone communications based on the IMS network. Equipment is provided for use. It is a regular ADSL modem, but with a built-in SIP client. But we have a CISCO 2951 with raised telephony. The thought arose whether it was possible to set up such a telephone number without Beltelecom equipment and directly in the router. When analyzing the settings in the modem, the following became clear. VoIP is supplied via a separate PVC (VCI/VPI=2/35) in IP/DHCP mode:
The modem receives IP and gateway settings via DHCP.
It is important for us to remember the gateway address for further configuration on CISCO.
When concluding a contract, the following information is provided:
Phone number: +37517xxxxxxx
Login:
[email protected]
You also need to know the password for the IMS service: passIMS
. I have ADSL2 and ADSL2 High-Speed WAN Interface Cards installed in my Cisco router.
First we set up the connection via the required PVC (2/35).
interface ATM0/1/0.2 point-to-point ip address dhcp no ip proxy-arp ip nat outside ip virtual-reassembly in atm route-bridged ip pvc 2/35 encapsulation aal5snap
.02
in the interface name was chosen arbitrarily, since I there is already one connection on the same interface. sh int atm 0/1/0.2 make sure that the interface is up and the IP address is received.
The SIP server settings can also be seen in the modem if you first issue the following command in telnet: sendcmd 3 webd setconfig voippagedisp y
.
We will use one of the SIP servers, namely 10.56.0.9
.
Next you need to register the routes. ip route 10.56.0.9 255.255.255.255 10.233.64.1 ip route 10.56.0.10 255.255.255.255 10.233.64.1 ip route 10.56.0.11 255.255.255.255 10.233.64. 1 10.56.0.10
and
10.56.0.11
are the address of the RTP server serving the audio stream. Since ims.beltel.by does not have an entry in the DNS, we register it manually. ip host ims.beltel.by 10.56.0.9 Now we move on to the direct configuration of sip-ua. There is a peculiarity here: authorization must take place indicating the domain, i.e. like [email protected] Therefore, we also use the
number
. sip-ua credentials number +37517xxxxxxx username [email protected] password
PassIMS
realm ims.beltel.by authentication username +37517xxxxxxx password
PassIMS
realm ims.beltel.by retry invite 3 retry response 3 retry bye 3 retry cancel 3 retry register 5 registrar dns: ims.beltel.by:5060 expires 3600 auth-realm ims.beltel.by sip-server dns:ims.beltel.by:5060 connection-reuse host-registrar Successful registration will be indicated by the command: sh sip-ua register status Next We create a dial-peer for outgoing calls.
dial-peer voice 8017 voip description #toIMS# translation-profile outgoing fromIMS
destination-pattern 8017[2,3,5].T session protocol sipv2 session target sip-server session transport udp voice-class codec 1 dtmf-relay rtp-nte no vad It is also necessary to replace your internal number with the number issued by Beltelecom in order for the call to be serviced.
This is done via translation-profile
.
voice translation-rule 1 rule 1 /.*/ /+37517xxxxxxx/ voice translation-profile fromIMS translate calling 1 Since I use Cisco 6921 phones, for an incoming call the secondary
on the internal number. ephone-dn 1 dual-line number 1234 secondary +37517xxxxxxx no-reg both This way we receive a SIP number into our telephone network without additional third-party equipment and in digital form.
Update:
Recently, Beltelecom began working using the UDP protocol. Therefore, for incoming connections it will no longer be possible to enter a secondary number. It is necessary to do dial-peer with an incoming rule.
Something like this:
dial-peer voice 9192 voip description #Incoming_IMS# translation-profile incoming incomIMS session protocol sipv2 session target dns:ims.beltel.by session transport udp incoming called-number +37517xxxxxxx voice-class codec 1 dtmf-relay rtp-nte where
translation- profile incoming incomIMS
is a rule for matching the IMS number to your internal one to which you need to receive a call.
For example:
voice translation-rule 5 rule 1 /.*/ /1234/ voice translation-profile incomIMS translate called 5
Card activation methods
There are the following ways to activate “plastic”:
- Call the hotline.
- Through the Internet.
- At the ATM.
- Using a smartphone application.
By phone
To activate a debit or credit card, you need to call 8-800-200-30-30, and then follow a few simple steps:
- Press the “1” key on your phone to select the “Maps” menu.
- Press “5” and do everything automatically.
If automatic activation was not selected, a transfer will occur to the bank manager, who will have to provide the following data:
- 16-digit credit card number;
- Full name, series and passport number;
- date of birth;
- mobile phone;
- Secret word.
Linking to a phone number and setting a code word is carried out to protect against fraudsters and identify the client in the future. After this, the manager will activate the account and generate a PIN code.
Via ATM
The most reliable way to register “plastic” is to use an ATM of the desired financial institution. The procedure is quite easy:
- We insert the card into a special slot and enter the PIN code. If it is entered incorrectly three times, the “plastic” is automatically blocked, so you need to be extremely careful.
- After pressing “Enter” and “Next”, select “Menu” and then “Check balance”.
- Checking the balance. If the plastic card is linked to your phone, you can refuse to issue a receipt by ordering the account balance to be displayed on the screen.
- We take the already activated card.
In the future, you will be able to manage funds at your own discretion, because... After registration in the system, restrictions on operations are removed.
Through the Internet
Despite the fact that the company does not officially provide an activation method via the Internet, you can use a little trick that will make the task much easier. To do this, just do the following:
- Register with Alpha Click, top up your mobile phone balance, transfer money to another account, or order free details.
- The card automatically becomes active.
Using a smartphone app
To use this method, you need to download the official application on the Alfa Bank website or through the Google Play service, then install it on your smartphone. After installation, you will have to enter the card number and perform any operation: transfer of funds, top up your mobile operator balance, etc. After this, the card is activated.
What to do?
The error may appear in third-party (user-installed) or system (pre-installed) applications. The following actions depend on which application and in what situation throws the error. If the notification appears with some frequency or when you launch a program you have installed (Viber, Talking Tom, Cool Reader, etc.), use the tips from these instructions. And if the problem is with system ones, which often appear on the screen and do not allow you to interact with Android, I advise you to additionally read the recommendations for elimination using the links provided. From the list, select which applications are causing the problem:
- — one or more applications from the Google Apps complex (Gmail, Calendar, Google Play Games, etc.);
- — related to updates to Google Play;
- — “Phone” application;
- — is responsible for setting up the graphical interface.
In addition, system applications are connected to each other, which means that an error in one can affect another. So, for example:
- a problem with settings (com.android.settings) may affect com.android.systemui;
- "Downloads" may affect "Google Play";
- "Google Play" is associated with the "Google Services Framework";
- The Google app is associated with com.android.systemui.
I also want to note that the cause of all the troubles may be a third-party, unoptimized program recently installed (or recently used/updated) on the device.
From my experience, I will say. The error indicated any application, but not the one that was the culprit. This malware turned out to be a constantly updated “news feed” that “devoured” the smartphone’s resources and prevented the normal operation of all other programs.
Distribution of IMS in Russia
In 2004-2005 The first demonstrations of IMS capabilities (Siemens and Ericsson companies) took place in Russia.
In 2006, Siemens opened an IMS demo center in St. Petersburg, where various services were demonstrated:
- Call&Share,
- Push And Talk Over Cellular,
- Mobile Presence Manager,
- Group Management,
- Instant Messages Center, etc.
In 2009, MGTS planned to implement IMS and complete the project in the analog segment in 2011, but due to the crisis, the project was only partially implemented. In particular, in 2010, only part of the analogue telephone exchanges were transferred to digital format, and the core of the network was installed. At the beginning of 2012, MGTS launched the first corporate service based on IMS into test operation; the service was planned to be launched commercially in March 2012. The first service was the scalable IP-Centrex service.
Earlier, in 2011, the macro-regional branch "South" of OJSC Rostelecom used the Alcatel-Lucent IMS solution to transfer the existing fixed network to an IP architecture with support for VoIP technology and other modern services.
In addition, in August 2012, the macro-regional subsidiary "Ural" of OJSC Rostelecom requested quotations for the right to enter into an agreement for the project "Development of a platform for the development and delivery of services and IMS core elements."
Definition of IMS
IMS is a software and hardware complex that is a key component of almost all Next Generation Network (NGN) IP networks that support SIP telephony (SIP, Session Initiation Protocol) applications, and is intended to ensure standardization of multimedia services across all interconnected networks. Thanks to its universal architecture, the same IMS platform can be used for applications and services in mobile networks of all generations (2G, 3G, 4G), as well as in fixed networks.
Moreover, it was in fixed-line networks that the IMS concept initially appeared - as a tool for reducing the number of networks of large operators (and, accordingly, costs) through migration to IP (a large-scale project of the BT Group (formerly British Telecom) in the mid-2000s). Later, as LTE took off, the main interest in IMS shifted towards supporting voice (VoLTE) and “enhanced” multimedia services (RCS).
The IMS network allows you to create several key mechanisms for interconnection between networks, instead of creating separate agreements for each service separately. This avoids duplication of functions and reduces operator costs.
One of the most important drivers for the implementation of IMS is the need to support voice services over LTE (VoLTE) networks.
Disabling IMS to improve power saving
The problem with modern gadgets is that they constantly require charging.
While looking for a solution to the problem of how to reduce battery consumption, I came across this: Economy mode for a 3G network. When using 3G mode and if you do not use the SIP protocol, you can reduce energy consumption for communication by disabling the mandatory IMS registration in the network. To do this: 1. In the dialer, dial the code *#*#4636#*#*; 2. In the menu that opens, select “Phone information”; 3. Click the “Mandatory IMS registration” button, it should become “disabled”. 4. We fix the result by rebooting. What is IMS? IMS is a solution for implementing services in IP-based communication networks, which represents a transition from classical telecommunications technologies to Internet technologies. Sometimes referred to as an acronym for an IP multimedia subsystem service architecture, it can provide the basis for network convergence, rapid deployment of new services, and cost savings through the use of open standards. The IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) was developed by the 3GPP (3G Partnership Project) industry committee for the use of IP cores in 3G networks and is now used by the joint technical committee TISPAN as a key element of the Next Generation Networks (NGN) infrastructure. The problem at the end of 2005 was the lack of standardization of mobile devices under IMS. As far as I understand, this is relevant for phones without LTE. I turned off this option on the SKB on the phone, I’ll watch it
Well, maybe someone else will need it, in case someone doesn’t know yet
>Voice over LTE (VoLTE)
AIBEILE application error ID or password error
This error is typical for the native AIBEILE application for watch models whose ID starts with 4700, 1703 and similar ones.
Typically, the default ID and password 123456 are used to log into the application. If you changed the password to a more complex one, check that it is spelled correctly. Through us you can reset your password to a standard one for a fee.
If this is your first time trying to log into the application, you see this error and the password 123456 does not work, then the ID number must be added to the application.
Your seller can add an ID number to the application database and start using it for free, and we also provide an adding service, but on a paid basis.
Session processing
One of the most important features of IMS that allow a SIP application to be dynamically and differentially (based on the user profile) triggered is implemented as a filter signaling mechanism and forwarded in the S-CSCF.
The S-CSCF may apply filtering criteria to determine whether to forward SIP requests to the AS
It is important to note that originator services will be applied on the originator network, while terminating party services will be applied on the termination network, all in the respective S-CSCFs.
Initial filter criteria
An initial filtering criteria
(IFC) is an XML based format used to describe control logic. IFCs represent a user's initialized subscription to an application. They are stored in the HSS as part of the IMS subscription profile and loaded into the S-CSCF upon user registration (for registered users) or demand processing (for services, acting as unregistered users). IFCs are valid for the entire registration period or until the user profile is changed.
The multifunctional complex consists of:
- Priority—Determines the trigger check order.
- A trigger point is a logical condition(s) that is tested for the initial SIP request creation dialog or standalone SIP requests.
- Application Server URI - Specifies the application server to be directed to when matching the launch point.
There are two types of IFCs:
- General - During initialization, only the reference number (general MFK number) is assigned to the subscriber. During registration, only the number is transmitted to the FU, and not the entire XML description. The full XML will be previously stored on CSCF.
- Unshared - upon initialization, the entire XML description of the MFCA is assigned to the subscriber. During registration, the entire XML description is sent to the CSCF.
APN for watch
To send mobile Internet settings to your watch, you need to send a regular SMS from your smartphone with this text from your telecom operator, preserving the punctuation, to the phone number on the watch.
Mobile Internet settings for different telecom operators:
MTS: pw,123456,apn,internet.mts.ru,mts,mts# Beeline: pw,123456,apn,internet.beeline.ru,beeline,beeline# Megafon: pw,123456,apn,internet,gdata,gdata# Tele2: pw,123456,apn,internet.tele2.ru# Yota: pw,123456,apn,internet.yota#SMARTS: pw,123456,apn,internet.smarts.ru#BaikalWestCom: pw,123456,apn,inet. bwc.ru,bwc,bwc# Motive: pw,123456,apn,inet.ycc.ru,motiv# Fly: pw,123456,apn,internet.letai.ru,,#
In response, you should receive a confirmation SMS message confirming acceptance of the settings marked OK.
How to log into your Google account on your device if you have access to settings
Some users tried to recover their forgotten Google account data using an SMS message. In this case, it is possible to log in, but after some time after completing the settings, the device reboots again and it is no longer possible to log in. If you're still at the stage where you can access your device's settings, you're in luck. The following instructions will help you remove your account from your device and create a new one.
- Open Android settings.
- Find the item “Accounts” or “Accounts”.
- Click on it and select your Google account.
- Then find the button that is responsible for deleting your account and click it.
Confirm deletion. Now you can reboot your device without fear of encountering the system message Log in to one of the profiles of the owner of this device. You can also add a new profile in the same section. To do this, click the “Add account” button. Now you will definitely write down important data from your account in a separate notebook, which will always be in one place.
Adding a Google Account
What to do if there is no access to the system?
The following instruction is an undocumented method to bypass the Android device locking algorithm - FRP Lock. To implement it, you will need a regular Micro-SD flash drive (the volume is not important). It needs to be inserted into your smartphone.
Another important feature is the need to insert a USB flash drive while the device is turned on. If the battery location and case features do not allow you to do this, you will need an OTG cable
With its help, you can connect a flash drive to the connector intended for charging the battery. When you insert the flash disk into the desired cell, a system message will appear on the smartphone screen. In it, the system asks the user if the default memory on the device needs to be changed. Click “Yes”. The system takes us to the settings section, where we need to select the default memory. Select "Applications and Media" in this window. The device will again take us to the “Applications” section, which are located in the “All” tab. Find the “Settings” application here and click on it. In this window, scroll down and find the “Run” button. The system displays to us the desired device settings. Here again select “Accounts”. Select the desired account and click the “Delete” button. Confirm your actions. Next, go back and select “DRM licenses”. In the next window, also select “Reset DRM” and confirm your actions.
Reset DRM settings
Now reboot your device. Make sure that the message Sign in to one of the device owner's accounts no longer appears. Create a new Google account and record the data from it in a safe place.
Method 2: Check if there are any app updates
In some cases, you will see that the IMS service is stopped due to outdated applications. As a result, this can cause various conflicts with the OS. In some cases, this may also affect the functionality of some applications. So, in this case, you should see if there are any updates for the applications. If yes, you should install them. To do this, you must follow the following steps.
- First, unlock your respective Android device and open the Google Play Store app.
- After opening the Play Store application, you must click on the menu button . It is located towards the top left corner and select the option called “ My apps and games ”.
- Click on the option called “ News” and then select “ update ”.
- Then you can click on Update All and wait for the update to complete.
- Now you can reboot your device and see if the problem is resolved.
Global IMS equipment market: main trends and forecasts
In the market of ready-made IMS systems in 2012, there are 7 largest vendors:
- Acme Packet,
- Alcatel Lucent
- Ericsson,
- Genband,
- Huawei
- Nokia Siemens Network (NSN) and
- ZTE.
At the end of 2012, the positions of the main manufacturers of equipment for IMS networks changed slightly. In particular, Alcatel-Lucent managed to push Genband out of second place. The market leader is still Huawei.
According to a survey of service providers conducted by Infonetics Research in 2012, the key drivers for the implementation of IMS were the deployment of LTE networks, as well as the ability to provide converged services based on IMS and the creation of a single standard.
Constraining factors for development:
- development of OTT services;
- high cost and duration of network deployment;
- technological difficulties with network deployment;
- difficulties in the development of FMC related to legislative regulation of the activities of mobile and fixed-line operators;
- fragmentation of the frequency spectrum for LTE networks.
2011
According to Infonetics Research, sales of equipment for IMS networks grew by 50% in 2011. Half of this growth occurred at the expense of North America: the driver was the launch of LTE networks by the American operator Verizon Wireless, which used the IMS platform from NSN.
IMS - IP multimedia subsystem
Details Parent category: 3G Category: Services in 3G networks
IMS provides:
- Real-time transmission of speech, video, multimedia
- Audio and video conferences
- Content delivery (video, audio, multimedia) – Content Delivery Services
- Streaming video, audio, multimedia – Content Streaming Services
- MMS
Rice. 1.
Services available in the CS, PS and IMS domains are shown in Fig. 2.
Rice. 2.
An example of an IMS session with service modernization is shown in Fig. 3.
Rice. 3.
Examples of several IMS sessions simultaneously are presented in Fig. 4.
Rice. 4.
Example of IMS PTT (Push-to-Talk) service - fig. 5.
Rice. 4.
The IMS architecture is shown in Fig. 5.
Rice. 5.
HSS – Home Subscriber Server Provides:
- HLR/AuC functions for CS domain
- HLR/AuC functions for PS domain
- Authentication, authorization, service profile management, localization functions for IMS (S-CSCF address)
Interface Cx (HSS – CSCF):1. Subscriber authorization during registration (I-CSCF - HSS) 2. Request for authentication vectors for the subscriber (S-CSCF - HSS) 3. Subscriber registration (status: registered/unregistered) (S-CSCF - HSS) 4. De-registration on initiative network (HSS - S-CSCF) 5. Location request (I-CSCF - HSS) 6. Subscriber profile update (HSS - S-CSCF).
P-CSCF – Proxy Call Session Control Function, an intermediary for interaction with subscriber terminals. The main tasks are subscriber authentication and account creation (on the same network as GGSN).
S-CSCF – Serving Call Session Control Function, the central node of the IMS, processes all SIP messages exchanged between endpoints (in the home IMS). I-CSCF – Interrogating Call Session Control Function, an intermediary for interaction with external networks. The main tasks are to determine the privileges of an external subscriber to access services, select the appropriate application server and provide access to it, define the S-CSCF. Processes requests to establish incoming SIP calls:• to home network subscribers;• to roamers located in this network. Processes requests to register “its” subscribers by assigning S-CSCF.MGCF - Media Gateway Control Function, manages transport gateways. Broadcasts messages of SIP and ISUP protocols. MRF – Media Resource Function, includes:
- MRFC (controller), controls the multimedia resource processor,
- MRFP (processor) provides the implementation of services such as conference calls, notifications, and transcoding of the transmitted signal.
BGCF – Breakout Gateway Control Function, an element that controls the forwarding of calls between the circuit switching domain and the IMS network. Performs routing based on telephone numbers and selects a gateway in the circuit switching domain through which the IMS network will interface with the PSTN or GSM.
The place of IMS in the mobile network is shown in Fig. 6.
Rice. 6.
SIP – Session Initiation Protocol
The application layer protocol defines how a user session that includes multimedia elements such as video or voice is established, modified, and terminated. SIP is one of the protocols underlying Voice over IP. SIP has been established as a 3G signaling protocol and a permanent element of the IMS architecture. The protocol is simple, all protocol requests are formed based on text.
An example of a SIP call through a SIP proxy server is shown in Fig. 7.
Rice. 7.
SIP methods are given in table. 1.
The classes of SIP response codes are discussed in Table. 2.
Briefly about IMS
IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem) is a specification for the transmission of multimedia content in telecommunication networks based on the IP protocol. Its authorship belongs to the international partnership 3-d Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), which united the European Telecommunications Standardization Institute (ETSI) and several national standardization organizations. IMS was originally developed in relation to the construction of 3rd generation mobile networks based on the IP protocol. The concept was subsequently adopted by the ETSI-TISPAN committee, whose efforts were aimed at specifying the protocols and interfaces necessary to support and implement a wide range of services in fixed networks using the IP protocol stack. Currently, the IMS architecture is considered by many operators and service providers, as well as equipment suppliers, as a possible solution for building next-generation networks and as the basis for the convergence of mobile and fixed networks on the IP platform. The principle on which the IMS concept is built is that the delivery of any service is in no way related to the communications infrastructure (except for bandwidth limitations). The embodiment of this principle is the multi-layered approach used in building an IMS. It allows you to implement an access technology-independent open service delivery mechanism, which makes it possible to use third-party service provider applications on the network. In Table. 1 shows a list of all interfaces of the IMS subsystem (including interfaces for interaction with the LTE access network), and Fig. Figure 1 shows the overall network architecture.
Table 1:
Fig.1 (IMS network architecture):
Let's look at the basic elements in more detail.
1. Call Session Control Function (CSCF) – session control function
There are 4 different types of CSCF - proxy CSCF (proxy CSCF - P-CSCF), serving CSCF (serving CSCF - S-CSCF), requesting CSCF (interrogating CSCF - I-CSCF) and emergency CSCF (E-CSCF) .
Each CSCF performs its own specialized tasks. Their general role is to participate in the processes of registering a subscriber terminal in the network, establishing a session and providing a SIP routing mechanism.
In addition, all CSCFs can generate tariff data and send it to offline charging functions.
a) Proxy Call Session Control Function (P-CSCF)
P-CSCF is the user entry point into the IMS. The user terminal (UE) forwards all IMS signaling traffic to the P-CSCF. Likewise, all signaling traffic generated by the network towards the UE is sent through the P-CSCF.
There are 5 unique missions performed by the P-CSCF:
- SIP compression,
The SIP protocol is a text protocol and includes a large number of headers, parameters, extensions, etc. Considering the textual basis of the protocol, the size of SIP messages significantly exceeds the size of messages of binary protocols. Accordingly, to speed up the session establishment procedure, mandatory support for SIP compression between the UE and the P-CSCF is required. The compression mode is enabled by the P-CSCF if the UE indicates the need for it.
- Integrity control and confidentiality protection of SIP signaling through the use of IPSec or TLS.
- Interaction with PCRF.
- NAT management (SIP ALG functionality – application level gateway).
Considering that in many communication networks subscriber terminals (UE) are located behind a NAT, which modifies the information of all packets passing through it at the IP/port network level, a problem arises due to the fact that the classic type of NATing does not take into account IP information at SIP and SDR levels. Truly comprehensive IMS access (the ability of a UE to interact with a P-CSCF regardless of the access medium) requires that the IP information in the SIP/SDP and user plane matches the information at the network (IP) layer (from the public IP addressing pool). For IP modification at the user plane level, the P-CSCF manages the access network gateway, which provides IP modification at the user plane level.
- Emergency call detection.
The task of the P-CSCF in this case is to detect an emergency call request and select an E-CSCF to handle this emergency call.
b) Interrogating Call Session Control Function (I-CSCF)
I-CSCF is the point in the operator's network for all incoming connections to subscribers of this operator. The main task performed by the I-CSCF is to assign the S-CSCF based on data received from the HSS.
S-CSCF assignment occurs when a user registers or in a situation where an unregistered user receives a SIP request for a service related to an unregistered state (for example, voice mail).
c) Serving Call Session Control Function (S-CSCF)
The S-CSCF is the central point of the IMS. It provides the registration procedure, routing decisions, session state machine management, and user profile storage.
When a user submits a registration request, it is ultimately routed to the S-CSCF, which initiates the authentication procedure and downloads the user profile from the HSS. Having received and verified the data, the S-CSCF confirms the registration, after which the user can generate and accept IMS requests.
S-CSCF uses the information contained in the user profile to decide when and which AS to connect when receiving a SIP request from the user. In addition, the user profile may contain instructions about the type of media policies that the S-CSCF should apply. For example, it may indicate that only audio components are available to the user, but video components are not available.
After the S-CSCF receives an outgoing (UE-originated) or incoming (UE-terminated) session request, the S-CSCF is responsible for making decisions about its further routing. For example, upon receiving an outgoing session request (UE-originated), the S-CSCF decides whether it needs to connect the AS before further routing the request. After interacting with the AS, the S-CSCF will either continue the session in the IMS domain or forward it to another domain (CS or IMS of another operator). If the UE uses MSISDN to address the called party, then the S-CSCF converts the MISISDN to SIP URI format before forwarding it further because IMS does not route requests based on MSISDN numbers. Similarly, the S-CSCF accepts all requests that will be terminated at the UE. Even though the S-CSCF knows the IP address of the UE (after the registration procedure), it routes all requests only through the P-CSCF, because The P-CSCF may enforce access security policies.
Additionally, the S-CSCF may send charging information to the OCS to provide on-line charging.
d) Emergency Call Session Control Function (E-CSCF)
E-CSCF is a dedicated functionality for processing emergency requests - calling the police, fire brigade, ambulance.
The main task of the E-CSCF is to select the appropriate public safety answering point (PSAP) to which the incoming request should be forwarded. Typically, the selection criteria for a PSAP are the user's location and the type of service being called.
2. Application Servers (Application Server – AS)
Strictly speaking, Application Servers (AS) provide value-added multimedia services and are not IMS objects, because are located in the interaction model at a higher level. AS are hosted either by an operator in the user's home network or by a service provider. Main functions of AS:
- the ability to process SIP sessions received from IMS;
- the ability to create an outgoing SIP request;
- ability to generate tariff data.
The services provided are not limited to pure SIP services. The operator can provide, incl. CAMEL (customized applications for mobile network enhanced logic) and OSA (open service architecture) services for its IMS subscribers in accordance with 3GPP TS 23.228.
Thus, by AS we mean SIP AS, OSA service capability server (SCS) and CAMEL IP multimedia service switching function (IM-SSF).
From the S-CSCF point of view, the SIP AS, OSA SCS and IM-SSF elements are the same type of modules. Since a user can have multiple services, there can be multiple ASes in each user's profile. One or more ASes can be involved in one session. For example, an operator may have one AS to provide voice supplementary services (for example, the service of forwarding all incoming voice calls from 17:00 to 19:00 to voicemail) and another AS to provide voice call continuity service (handover VoLTE in 2G/3G CS call).
3. Controller and Multimedia Resource Processor (Media Resource Function Controller - MRFC, Media Resource Function Processor - MRFP)
MRFC and MRFP provide services such as conference calls, playback of voice messages (announcement), transcoding of media streams. MRFC – processes SIP signaling to/from S-CSCF/AS and manages MRFP. MRFP - provides user-plane resources in accordance with commands received from MRFC:
- mixing media streams (for multiple parties);
- generation of voice messages (announcement);
- media stream processing (transcoding, analysis,...)
4. Interworking function between IMS and Circuit Switched (CS) domain
Rice. 2:
To route a call to a circuit switched domain (CS domain), the S-CSCF forwards the SIP request to the BGCF, which selects the appropriate CS domain. In this case, the CS domain can be selected both on the current node (in accordance with the location of the user who made the call) and on another network. If the CS domain is selected in another network, the BGCF forwards the request to the BGCF of this network. The request is then sent from BGCF to MGCF. The described option allows you to route the signal and media stream over the IMS network as close as possible to the called subscriber.
When a SIP request reaches the MGCF, it performs protocol conversion (SIP protocol on the one hand and ISDN user part - ISUP on the other) and then sends the converted message to the SGW CS of the domain. SGW performs two-way transport layer signaling conversion (SIGTRAN IP/SCTP/MxUA on one side and SS7 MTP on the other side). SGW does not handle application level signaling (ISUP). In Fig. 2 SGW is part of IM-MGW.
The MGCF also controls the IM-MGW. IM-MGW provides a user-plane link between IMS and CS domains. It terminates TDM channels of the CS domain on the one hand and the media stream of the IMS domain on the other; performs their conversion, transcoding (if necessary) and processing of user signaling.
In addition, the IM-MGW can generate tones and announcements to users in the CS domain.
Signaling related to incoming calls from the CS domain (ISUP) towards IMS users is sent to the MGCF where it is converted into SIP requests, which are then forwarded to the I-CSCF for termination.
5. SMS interaction function
Fig.3:
IP short message gateway (IP-SM-GW) connects the most common mobile messaging technology SMS with IMS messaging. When an SMS is sent to an IMS user, the SMS is routed over the SS7 signaling network to the IP-SM-GW, which places the received SMS as a special type of content in the SIP MESSAGE and forwards it to the S-CSCF for further routing. This allows you to deliver SMS messages to users who are registered in non-3GPP mobile IP networks (Wi-Fi, WiMAX), and can also be considered as an alternative to traditional methods of delivering SMS messages (CS, GPRS).
IP-SM-GW also allows you to deliver SMS in the opposite direction (from IMS network subscribers to CS 2G/3G network users). When an IMS subscriber sends a SIP message containing SMS as a special content type, the IP-SM-GW extracts it and forwards it to the SMS center (SMSC) for further delivery over SS7 networks. This type of interaction allows you to provide all existing SMS services (including services with additional payment) to subscribers registered in IMS networks. This functionality is called SMS over IP (3GPP TS 23.204).
Additionally, IP-SM-GW can support “native” service for interaction between SMS and SIP-based applications. In this case, the SMS is converted into a native SIP request and the IMS UE does not require support for SMS technology.
There is a limiting factor that needs to be taken into account, namely, the size of the SIP message (RFC3428) must be at least 200 bytes less than the MTU (maximum transmission unit). If the IP-SM-GW receives a concatenated SMS message (a group of standard-length messages that together form one long message) and the SIP MESSAGE size exceeds the possible limit, the IP-SM-GW must use session mode.
Session mode involves the initial establishment of a session between the IMS UE and the IP-SM-GW, for which the IP-SM-GW sends a SIP INVITE. Once a session is established, the message session relay protocol (MSRP) is used to deliver the IMS message to the UE.
6. Function of interaction between IMS networks of different telecom operators
Fig.4:
The interaction function between IMS networks of different telecom operators is implemented through the Interconnection Border Control Function (IBCF) and the Transit Gateway (TrGW). The following tasks are solved:
- Translation between different versions of IP (IPv4, IPv6) used on operator networks. In this case, IBCF modifies SIP and SDP data, allowing users using different IP versions to communicate with each other.
- Transcoding in a situation where end-user applications do not have a common codec that can be used (for example, transcoding between AMR and G.722). The transcoding service can be enabled proactively (before a request to establish a session with the called subscriber) or reactively (after the session is interrupted by the called subscriber) - 3GPP TS 23.228.
- Hiding the network topology. In this case, IBCF performs encryption/decryption of all message headers that contain information about the network topology.
- Filtering information in SIP messages. In this case, IBCF removes or modifies some SIP headers before routing messages towards third-party networks.
- Choosing a direction.
- CDR generation.
- NAT/Port translation – TrGW performs modification of IP headers of user traffic packets (RTP, etc.)
7. IMS Access Gateway (IMS-AGW – Access Gateway)
In private (for example, home and office) fixed networks, the user terminal (UE) may be located behind NAT and firewall installed on network devices that are access points to such networks (customer premise equipment - CPE). At the same time, NAT does not modify / natify information at the SIP / SDP levels.
To solve this problem, the P-CSCF contains the SIP ALG (application level gateway) functionality, which provides control of the IMS-AGW. A SIP INVITE request from a UE with a private IP address reaches the P-CSCF, the ALG functionality of which assigns a public IP address, binds it to a SIP session, performs NATing (replacing private IP addresses at all protocol levels, including IP, SIP, SDP), carries out its further routing and informs the access gateway about the created connection. When a media stream arrives between two user terminals (UE), the access gateway will NAT RTP packets to/from public/private address spaces.
8. Security Gateway (SEG)
The security gateway is located on the border of the operator's domain zone and ensures its protection. All inter-domain traffic must pass through SEG. SEG provides confidentiality, data integrity and authentication in accordance with 3GPP TS 33.203.
9. Location Retrieval Function (LRF)
The LRF assists the E-CSCF in IMS processing of emergency calls by providing location information about the user terminal (UE) that initiated the emergency call, which is used to select the emergency service provider (PSAP) to which the session should be forwarded. To obtain information about the user's location, LRF can have a built-in location server or have GMLC (gateway mobile location center) functionality - an interface to an external location server.
To select the appropriate PSAP, the LRF may contain an RDF (routing determination function) function, which is used to select the PSAP address based on the user's location information.
LRF can provide support for other local regulatory parameters, such as emergency service routing number, location number, PSAP SIP URI, PSAP TEL URI,…
10. Enhanced Mobile Switching Center - Enhanced MSC Server (eMSS)
eMSS is a 2G/3G MSC that has P-CSCF functionality in the IMS direction.
When a user registers in a 2G/3G network, eMSS performs registration in the IMS domain on behalf of the user, which allows a CS network user who does not have access to the packet network to gain access to IMS services.
When a user makes a mobile originating call, eMSS converts the legacy CS call into an IMS session request and forwards it to the IMS system. Similarly, when someone makes a call to a user served by eMSS, the incoming call (mobile terminating call) is routed to the IMS platform, which carries out the established incoming call control procedure, including HSS interrogation, and forwards the SIP request to the eMSS, which in turn converts the protocol IMS session management into the CS call control protocol.
eMSS allows you to provide a service that is truly independent of the access type (CS, IP-CAN, legacy), since the provision of the service is always provided by the IMS platform. This allows users to migrate from 2G/3G CS networks to IMS and back.
11. Access Gateway Control Function (AGCF)
AGCF – is an entry point for users of PSTN/ISDN networks (analog and ISDN phones). It performs the following functions:
- access gateway media gateway (MGW) control;
- interaction with the resource and access management subsystem;
- interaction with the network connection subsystem to obtain information about the line profile;
- providing signaling interaction between SIP signaling on the one hand and analogue telephone / ISDN signaling on the other hand.
From the point of view of the IMS platform, AGCF looks like P-CSCF and provides the corresponding functionality (management of the SIP registration procedure, etc.).
12. Tariffing functions
The information required for charging is collected by the charging functions of various IMS modules from the SIP request. In this case, online billing is possible (in this case, the billing function requests permission from the billing system to process the SIP request) and offline billing (in this case, the billing function always allows processing of the SIP request, sending the collected billing information to the billing system to generate CDR records).
Depending on the IMS configuration, different tariff schemes for various services are possible. In this case, the pricing logic is controlled based on the activation of certain triggers. Triggers can be:
- requests for creating, modifying and terminating a session (sessionbased charging);
- any SIP transaction, for example, MESSAGE, PUBLISH, SUBSCRIBE (eventbased charging);
- certain SIP headers and SDP information.
Rice. 5:
The charging functions of all IMS modules, as well as access modules, can interact with an offline charging entity (CDF) using a diameter-based Rf interface (3GPP TS 32.299).
Based on information received from the charging functional blocks of all IMS modules, the CDF creates CDR records that are forwarded to the charging gateway function (CGF) via the Ga interface (3GPP TS 32.295). Next, CGF processes the received CDRs and forwards them to the billing system using the Bx interface (3GPP TS 32.240).
Prepaid services require online billing. This means that the IMS network must request OCS before authorizing a user to use a particular service. OCS is responsible for monitoring the user's account in real time, authorizing the user to use the service and debiting the balance from the user's account for services received. Only three IMS modules (S-CSCF, AS, MRFC) communicate with OCS using the Ro interface. In addition to IMS modules, non-IMS modules can interact with OCS. In particular, SGSN uses the CAMEL application part (CAP). In addition to credit control (on-line charging), OCS can create CDR records similar to CGF.
13. Home Subscriber Server (HSS) function
HSS is a repository of subscriber and service-related data. It contains authentication center functionality (AUC), LTE functionality (SAE-HSS), GSM/UMTS functionality (HLR), IMS functionality (IMS-HSS), data repository functionality for charging and quality policy management (SPR). HSS can also be used to store application server (AS) data.
Rice. 6:
14. PCC function of policies and charging rules (Policy and Charging Rule Function - PCRF)
The PCRF is responsible for generating quality policies and managing billing based on session information received from the P-CSCF.
Session establishment in IMS is ensured by the exchange of signaling messages using SIP and SDP, including negotiation of media characteristics (codecs, IP addresses, port numbers). If the operator uses PCRF on its network, P-CSCF forwards it the necessary SDP information, on the basis of which it creates policies and charging rules, and also authorizes IP streams of the corresponding media components, mapping SDP data to IP QoS parameters for the access network gateway, for example, P-GW/PCEF.
Based on the available information, PCRF applies PCC-generated policies and charging rules on the access network gateway (P-GW/PCEF), creates and modifies virtual connections to carry media traffic (EPS bearer). In addition, PCRF receives events from the transport layer, for example, when a radio connection is lost, informing the P-CSCF about these events, which uses the received information when generating charging data and closing the IMS session on behalf of the user.
In addition, PCRF can be used to exchange charging identifiers that allow the operator to correlate CDRs generated by the access network and the IMS network; deliver charging method (duration, volume, both) to the access network; rating group information; on-line / off-line charging activation commands; addresses of on-line / off-line tariff systems; required level of reporting based on service and rating-group.
Rice. 7:
Security aspects of early IMS and non-3GPP systems
The security assumed to be defined in TS 33.203 may not be available for some time, especially due to the lack of USIM/ISIM interfaces and the prevalence of devices that support the IPv4 protocol. In this situation, to provide some protection against the most significant threats, 3GPP defines some security mechanisms that are informally known as "early IMS security" in TR33.978. This mechanism is based on authentication performed during attachment network procedures, which links between the user's profile and his IP address. This mechanism is also weak because the signaling is not protected from the user of the network interface.
CableLabs, which has also adopted the IMS architecture but does not have USIM/ISIM capabilities in its terminals, published deltas in the 3GPP specification, where Digest-MD5 is a valid authentication option. Later, TISPAN also made similar efforts considering their fixed network sights, although the procedures are different. To compensate for the lack of IPsec capabilities, TLS was added as an option to provide the Gm interface. Later 3GPP Releases included the Digest-MD5 method, on the way to the common IMS-platform, but in its own and again a different approach. Although all 3 DIGEST-MD5 authentication options have the same functionality and the same functionality from the IMS terminal point of view, the implementations on the Cx interface between the S-CSCF and the HSS are different.
Fix: Unfortunately IMS service is stopped on Android -
Samsung builds its own user interface on top of Android and provides its own core applications such as Messages, Browser, Settings, etc. I n Multimedia S ubSystem is an architectural framework for delivering multimedia services to consumers . More recently, there have been many reports of users experiencing the "IMS Service Stopped" message appearing on their screens, sometimes randomly and sometimes while trying to call someone or send a message.
IMS service stopped with error message
What causes the "IMS Service has stopped" error message?
After receiving numerous reports from several users, we decided to investigate this issue and developed a set of solutions that have been tested to resolve the issue with the majority of users. Additionally, we have looked at the reasons why this may be caused and have listed them below:
- cache: All applications store a cache to reduce loading time. Cache memory reduces the time it takes to load a particular application by storing temporary files on the partition. However, over time this cache can become corrupted. This corrupted cache can cause problems with some Android apps, especially the messaging app, and prevent it from working properly. If the application does not work as expected, a message is displayed indicating that the IMS service has stopped working.
- Default Messaging Application: Depending on the region you live in and the network provider you use, there are certain configuration files that network providers apply before providing Internet, calling, and messaging services. It is possible that these configuration settings interfere with certain elements of the default applications and prevent them from working properly.
- Legacy apps: In some cases, legacy apps may not work properly with an updated version of Android. It is also possible that there were some bugs in the apps and they were fixed by the developers in updates and were not fixed in the legacy app.
- Outdated Android Software: It's possible that there was a bug in the Android software or the manufacturer's UI on top of the operating system that was fixed in an update, so if you haven't updated your Android to the latest version, you may encounter this error.
- Third-party messaging apps: Sometimes third-party apps can overtake the default messaging app and cause problems with the messaging service. If the messaging service is blocked or disabled by default, this message is displayed.
Now that you have a basic understanding of the nature of the problem, we'll move on to solving it. To avoid any conflicts, it is recommended that you follow the steps exactly and in the specific order in which they are provided.
Solution 1: Check for software updates
It's possible that there was a bug in the Android software or the manufacturer's user interface on top of the operating system that was fixed in an update. Therefore, at this stage we will check for software updates for mobile devices. For this:
- unlock your phone and open settings.
- Scroll down and tap " About Phone ".
- Click on “ Software Updates ” and select “ Check for Updates” option.
- If a new software update is available, click on " Download Now " which appears after the verification process is completed.
- Once the phone finishes downloading the update, it will prompt you to confirm the installation from Update Select " Yes and the phone will restart.
- The update will be installed and the phone will be launchbackVnormal Mode, check to see if the problem still persists.
Software Update Check Process
Solution 2: Check for app updates
Sometimes, if some applications are outdated, they can cause conflicts with the operating system and sometimes even with other applications. Therefore, at this stage we will check the Google Play Store for new app updates. For this:
- unlock your phone and open the Google Play Store app.
- Click on menubutton on Topleftcorner and select "My Applications GamesOption.
By clicking on the menu button in the Google Play Store - Click on the " Updates " and select the " Update " icon.
- Click on “ Update All” and wait for the applications to update and install.
- Check to see if the problem persists.
Solution 3: Changing the message configuration
It is possible that network operator configuration settings are affecting certain elements of your messaging application and preventing it from working as expected. Therefore, in this step we will disable the carrier network settings inside the messaging app. For this:
For ATT:
- open until default messaging app.
- Click on menu button on Toprightcorner and select "settings«.
By clicking on the menu button in the upper right corner - Now click on the “ Backup ATT Messages Sync” and select the “ Disable Sync” option.
- Launch your mobile again and check to see if the problem persists. Note: After restarting your mobile device, make sure that it has not been turned on automatically again. If so, simply disable it again and skip the restart process.
For rich communications:
- Open your default messaging app and click on the menu button on the top right corner. By clicking on the menu button in the upper right corner
- Select " Settings " from the list and click " Selected Chat Settings ".
- Click on Rich Communication Settings and uncheck Rich Communications From List.
- Start your mobile phone again and check to see if the problem persists.
Solution 4: Start in Safe Mode
Safe Mode disables almost all other applications installed on the phone except the default one. This may prevent other apps from interacting with the default messaging app and may help identify the problem. Therefore, at this stage we will start the device in safe mode. For this:
- Press the Power button and select the Power Off option.
- Once the device is completely turned off, switch it on and hold the power button for 2 seconds.
- When Samsunganimationlogo displays hold down "volumedown».
Samsung Animation logo on device startup - The word " Safe Mode" should be displayed in the below left corner of the screen if the process was successful.
- Check to see if the issue persists, if it is resolved, try deleting one third party app and then check if the message still appears
- You can continue this process until deleting the specific application problem is resolved.
Solution 5: Clearing the cache
Over time, the cache can become corrupted. This corrupted cache can cause problems with some Android apps, especially the default messaging app. Therefore, at this stage we will completely clear the cache from the partition. For this:
- Hold down the power button and select the “ OFF switch ”.
- Hold " Home Button and Volume Up " button at the same time and then press and hold " Power " button.
- When Samsung logo screen only appears " Power Key".
- When Android logo screen show release all keys screen may show Setup System Update for a few minutes before showing Android Recovery Options .
- Click «volumedownKey torubcachechapterHighlighted.
Navigate down to "Wipe Cache Partition Option" - Click Power button and Wait for the device to clear the cache partition.
- When the process is complete, swipe down the list through the “ Volume Down” button until Reboot System Now Highlighted.
- Tap " Power " to select the option and reboot your device.
- Once the device is restarted, check to see if the problem persists. Note: You must be very careful with this process because even a small mistake during this can result in your phone's software being permanently locked.