Mobile phone users often wonder how to exit Recovery mode on Android. Sometimes it happens that a recovery screen appears on the phone and there is no way to start the system normally.
When someone turns on or reboots their device, it automatically enters Android System Recovery 3e mode. Before fixing this problem, you need to understand what Recovery is and why this mode can start at the wrong time.
What is recovery mode?
What is the Android system recovery screen for? This feature on the device is used to enable several very useful options and can be an effective tool for customizing the phone in the hands of an experienced user.
One of the most useful options on the system recovery screen is the ability to reset the device to factory settings if you cannot access the operating system. This can be extremely helpful if your phone won't turn on properly, won't respond to touch screen touches, or won't allow you to access settings. The fact is that if for some reason the user fails to enter the options of his device, the ability to reset to factory settings will be blocked for him.
Recovery mode helps solve many problems associated with Android system malfunction. If you want to reset your device to factory settings using this function, you must first turn it off and then press and hold certain buttons.
Depending on your phone model, these could be volume keys, power keys, home keys, etc. This will boot your device into system recovery mode. Then you can erase all user data on your mobile device if you select the Wipe Data (or Factory Reset) option and confirm the reset using the Delete All User Data item. As a result, all files will be deleted from the phone.
Part 3: How to Boot into Recovery Mode on Android Phone
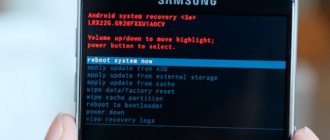
With Android developed, it is more than a tool that people use to call others or text messages. As you know, most Android devices now have a fairly simple Android recovery mode by default. And most of the recovery mode has six main functions: Reboot system now, Apply update from ADB, Apply update from external storage, Wipe data/factory reset, Wipe cache partition, Apply update from cache. With six functions, you can reboot your Android device, erase data, install updates to SD card, and so on. Next, we'll take a closer look at the four features of Android recovery mode. For more knowledge, please scroll down and read on.
Android Recovery Mode Option - Reboot System Now
Reboot System Now is an option that allows you to reboot your Android phone, your Android device will shut down and reboot into the commend interface. If your Android phone is frozen or has some errors, you can boot into Android recovery mode and reboot the system. When you boot into recovery mode, do something else and when you are done, you can also exit Android recovery mode by selecting this option.
Android Recovery Mode Option - Apply Update from ADB
ADB is an Android recovery mode tool, short for Android Debugging Bridge. To use this feature, you'd better connect your Android phone to your computer so that it can build a bridge between the two devices. Android Debugging Bridge allows users to perform some operations through the computer with your Android device. So it is widely used by Android app developers to fix app bugs. Moreover, ADB also allows you to use your computer to push and install updates to your Android phone, which depends on the connection between your phone and computer. But this feature is more suitable for app developers and may be difficult for those who have never touched it. If you need to use this tool, you can find step-by-step instructions on the website.
Android Recovery Mode Option – Wipe Data/Factory Reset
Wipe Data/Factory Reset is a very common and easy way to reset your Android device into Android recovery mode. When you select this feature, it will erase all your data including photos, videos, messages, photos and apps. And then it will return your phone to its original factory state. This is very convenient for you when you want to deal with your old Android phone. But if you just want to factory reset your phone to fix Android problems, make sure all your Android data has been backed up.
Android Recovery Mode Option - Wipe Cache Partition
The cache partition is temporary data which is mainly related to app installations and it will be stored in your Android phone. This will slow down your Android device and even make your phone unusable. But you can delete it by wiping the cache partition in Android recovery mode without losing any personal data or settings, which means you cannot erase them. So this is recommended to fix many common Android problems.
A simple way to solve the problem
If the device cannot exit from system recovery mode, then most likely this is due to a failure of one or more buttons used to access Recovery. For example, if the phone uses the volume down and power keys, a situation may arise where the volume button is malfunctioning and the device “thinks” it is pressed. This leads to the fact that during startup the phone thinks that the user is trying to start Recovery mode. First of all, you need to make sure that the physical buttons on your mobile device work correctly, and especially the volume keys. Sometimes it happens that visually they look good, but they do not function properly.
Before proceeding to the next step, it is highly recommended that you turn off your phone. It is not safe to remain in Recovery mode and manipulate the buttons, as this may lead to accidental deletion of information on the device. Next, you need to try to press the keys several times. If it turns out that they are stuck, then a few clicks can help them return to their original position.
After such manipulations with the buttons, you need to try to turn on the phone and check whether the operating system boots.
If the device starts up normally, you will need to back up all important information as soon as possible. If the phone becomes seriously faulty or physically damaged, it may lose all important data.
After you have created the backups, you can turn your device off and on again to see if it can start normally again. If your phone is no longer stuck on the system recovery screen, then the problem has been resolved.
How to switch to Recovery mode on Huawei and Honor
To enter Recovery mode on Huawei and Honor, you will have to perform a few simple steps:
- simultaneously hold down the power (turn on the smartphone) and volume up buttons;
- hold the keys down for several seconds;
- wait until the desired mode appears on the screen.
It is important to emphasize that you can only enter Recovery from a switched off device. If the phone is turned on, the function will not be launched, regardless of the users' wishes.
If the approach described above does not help achieve the desired effect, and the desired mode does not start on Honor, you should enter it in another way:
- simultaneously hold down the power and volume down buttons;
- hold the keys down until the desired result is achieved;
- go to using Recovery.
The fact that on older Huawei phone models the volume down and up buttons were replaced by a home key located between them deserves special attention. Sometimes you just need to press it.
If you have difficulty activating the function and opening the menu, you should hold down the keys for a longer time. Perhaps the difficulties lay precisely in the insufficient clamping time, so it is not difficult to open Recovery and cope with the difficulties.
Recovery mode can be stock or custom. Stock Recovery Mode is the first and original option that is installed initially on a smartphone and you can work with it immediately after purchase. This mode works on a stock smartphone or one already rooted, but not on a Galaxy smartphone that is flashed with custom firmware.
other methods
If the above steps did not help, the reason for the spontaneous boot of Recovery may not be related to a malfunction of the buttons. The failure may occur as a result of installing a third-party firmware (ROM), attempting to access the root of the phone, or installing a custom recovery module (for example, ClockworkMod or CWM). The installation was probably unsuccessful, so you might want to try again. Such operations must be performed with extreme caution as they can cause some serious problems, for example, if the steps are performed incorrectly.
When installing third-party software related to firmware and obtaining additional settings, you should always carefully study the accompanying documentation. It is usually published on the same web resources where users download the necessary files.
If Recovery mode crashes for no apparent reason, it is most likely a hardware issue related to the physical buttons on the device. To eliminate the small possibility that it is not software dependent, you should consider selecting the Wipe Data/Factory Reset option on the recovery screen. This feature will fix any errors or crashes, remove viruses, and return your phone to its default settings. As a result, all user information on the device will be irretrievably lost, since the backup option will not be able to be launched, but in some cases, such a radical method helps eliminate the problem.
You need to carefully check your phone for physical damage or liquid penetration. Damage is usually visible to the naked eye. When it comes to moisture intrusion, many phones come with built-in LDI (Liquid Damage Indicator) indicators that alert users if liquid has infiltrated that could cause damage. If all of the above tips did not help resolve the problem, then you should contact a specialist in repairing Android devices.
Do you want to install a custom ROM on Android or in other words a third party OS version like CyanogenMod? Most likely you will also need to install a custom recovery.
All Android devices come with a recovery tool pre-installed. This recovery software can be used to restore your device to factory settings, update the operating system, or perform other tasks.
Android devices already come with Google's recovery tool, which is often called "stock recovery." You can boot into recovery by pressing certain keys on your smartphone or tablet, or using the adb command, which will boot your device into recovery mode.
The recovery menu provides features that will help you restore your device, for example, from here you can restore to factory settings. Recovery mode can also be used to update OTA files. If you want to install new firmware on your device or restore the factory firmware, you will first need to enter recovery mode.
With stock recovery the system is limited. It can be used, for example, only to update OTA files and firmware from the manufacturer.
Custom recovery is a third-party recovery environment. This is similar to installing a custom firmware like CyanogenMod, but instead of replacing the operating system, it replaces the recovery environment.
The custom recovery environment will do the same as the stock one. However, it will also have additional features. Custom recoveries can often create and restore device backups. Custom recovery allows you to install custom firmware. ClockworkMod even provides a "ROM Manager" app that allows you to access many features from a running Android system - this app requires a custom recovery.
ClockworkMod Recovery (CWM) can create and restore NANDroid backups - backup copies of the entire file system of an Android device. ClockworkMod provides a ROM manager with a file browser that will allow you to view and install custom ROMs via ClockworkMod Recovery and manage and restore backups. It also has other additional features that will be useful when installing and working with custom ROMs.
Team Win Recovery Project (TWRP) is a push-to-use recovery environment. Unlike other recovery environments, including the stock one, where the volume keys are used for navigation and the power key for selection, this one uses an interface that can be used by tapping the screen. TWRP even supports themes. Just like CWM, TWRP provides the ability to install custom firmware and create and restore system backups, which is not available in stock recovery.
CWM and TWRP are two of the most popular custom recoveries, but other custom recoveries may only be available for some devices.
Custom recovery environments are useful if you install custom firmware, because... they provide the ability to backup data as well as restore it, which will undoubtedly be useful to you. You will have to unlock the bootloader on your device to install the custom recovery.
Although this function is hidden and requires the use of adb commands. You don't have to unlock the bootloader, install custom ROM, or even root to create or restore a full backup.
Install custom recovery if you want to install custom firmware or get a powerful backup tool. This action is often considered as a preparatory step before installing custom firmware, but it is not always necessary. For example, the CyanogenMod installer will also install ClockworkMod Recovery (CWM).
In general, custom recoveries are only needed if you plan to install a custom ROM. Most Android users won't even notice the differences between custom and custom recovery.
Every tablet or phone based on Android OS is equipped with the Recovery Mode recovery environment. It refers to the system part of the mobile operating system and allows you to perform specific procedures on the device that are not available in the regular menu. Let's look at what Android Data Recovery is, how to enter this mode and how to work with it.
Xiaomi
Xiaomi uses its own recovery menu.
To exit it, you first need to exit to the main menu by selecting Back to Main.
Then select Reboot.
Finally - Reboot to System.
The device will reboot normally. You can also select Power Off to turn off the smartphone.
Recovery from Team Win Recovery Project allows you to reboot your smartphone directly from the main page through the item of the same name.
If the English version is installed, use the Reboot button.
Do you still have additional questions? Ask them in the comments, tell us what worked for you or vice versa!
Standard/CWM/Philz
Select “Reboot system Now” - after which the Android smartphone or tablet will reboot.
TWRP
Go to the “Reboot” menu, and then select the “System” item
If you can't exit Recovery Android?
If for some reason your Android does not return to normal operation and returns to the Recovery menu, or you simply don’t understand what to do, then try the following:
- Press and hold the power button for more than 15 seconds
- Remove and reinsert the battery
- Wait until the Android device discharges itself
- Connect Android to the PC, in the ADB RUN program in the Manual Command -> ADB menu, enter the following command adb reboot normal (does not work on all devices)
Do you still have additional questions? Ask them in the comments, tell us what worked for you or vice versa!
That's all! Stay with the Android +1 site, it will be even more interesting! Read more articles and instructions in the Articles and Android Hacks section.
The smartphone will be turned off and automatically boot into normal mode.
Recovery menu is an additional menu, one might say secret, with which you can update the firmware or reset data on your smartphone. They shoved it away for a reason, but to prevent the user from inadvertently clicking where he shouldn’t. This article explains how to exit recovery on Xiaomi or Redmi.
Actually, the recovery menu is in front of you:
To exit it, select Reboot (selection - volume buttons, confirmation - power key).
Next - Reboot to System.
The smartphone will be turned off and automatically boot into normal mode.
If the power key doesn't work, try this: first select Reboot.
Wait 10-20 minutes until this item is selected automatically (this function is present in the firmware).
Next, do the same with the Reboot to System item - select it and wait.
The smartphone will reboot.
Another option is to press and hold the power key until the screen goes blank.
Next, the phone should boot into normal mode, and if it doesn’t turn on, turn it on yourself.
Finally, your firmware may use TWRP recovery. The menu is touch-sensitive; to reboot, select Reboot or “Reboot”.
As in previous cases, your Xiaomi or Redmi will boot into normal mode.
CAHEK80 replied: 2020-01-22 18:08:17
Hello! You are right about the truth, that the author is not telling the truth. I had this happen, without booting into the system it was thrown into recovery. But this happened to me due to quick firmware changes and tests of different mods, after which I did not clean the tails. so it jammed. and again, you are right, after the author’s words and what he doesn’t say, there is no point in helping.
I rebooted my phone and accidentally got into recovery mode. I can’t get out of it in any way: I click Reboot - it returns to the same menu, Wipe data - the same thing. Attempts to turn off the device do not help - the same menu with three buttons appears every time. What to do?
Karasev Evgeniy replied: 2020-01-22 16:03:55
Hello.
First, tell the whole truth: what and how did you do it?
You don’t get into that mode like that and get out very easily.
acidmist replied: 2020-01-22 16:12:11
Where are the complaints against me coming from? What is the point of keeping silent about something if I want to solve the problem, and especially to whom will I hide “my actions”? If you can't help, it's better to pass by
If you can't help, it's better to pass by
1619716888 | from Redmi Note 5
CAHEK80 | from Redmi 5 Plus
Karasev Evgeniy
Hello.
First, tell the whole truth: what and how did you do it?
You don’t get into that mode like that and get out very easily.
CAHEK80 replied: 2020-01-22 18:08:17
Hello! You are right about the truth, that the author is not telling the truth. I had this happen, without booting into the system it was thrown into recovery. But this happened to me due to quick firmware changes and tests of different mods, after which I did not clean the tails. so it jammed. and again, you are right, after the author’s words and what he doesn’t say, there is no point in helping.
CAHEK80 | from Redmi 5 Plus
Karasev Evgeniy
Hello.
This is why I can think that everything is not so simple here.
If the Redmi Note 5 device had crashed during the update (and it could have been installed overnight), it would have most likely happened when switching to Android 9 (that is, six months ago, not now, and even on a Chinese version with a patched bootloader).
Huawei eRecovery is a very useful feature for smartphones with the Android operating system. But often users have to figure out how to exit this mode correctly and safely.
Purpose of the recovery area
The Recovery Mode recovery environment is an indispensable tool for developers and engineers dealing with programming or customizing the Android OS. However, ordinary users of mobile devices often resort to it.
Considering what Recovery mode is, it is necessary to note its main capabilities:
- Resetting the gadget to factory settings (Hard Reset), when this cannot be done from the standard menu;
- Installation of custom firmware;
- Activation of Superuser rights;
- Creating a system backup with all user data and settings;
- Restoring Android using a previously mounted backup;
- Allocation of system partitions on an external micro sd memory card;
- Connecting the device to a computer to work with the ADB debugging bridge, etc.
It should be noted that you cannot do without Recovery on Android if you cannot enter the graphical menu of the operating system, as well as if your smartphone or tablet is turned into a “brick”.
How to enter the Recovery environment
Transferring a mobile device to Recovery mode can be done in several ways:
- Using a combination of mechanical keys;
- Via the ADB debug bridge;
- Through special software, which is installed directly on the phone.
In the first case, to enter Recovery Mode, a certain combination of the Power and Home buttons (if available) and the volume rocker are used. However, this combination may differ among different manufacturers. Thus, in almost all Nexus series smartphones, the resuscitation area is loaded using the Power + Volume Down keys. For Samsung, the current set is “Power” + “Home” + volume rocker sandwiched in the middle. The above steps are performed with the device turned off.
If you cannot find the required combination, you can open Recovery on Android using the ADB debugging bridge or its automated version ADB Run:
You can also get into recovery mode using additional software installed directly on the mobile device. One such application is Quick Boot. Just install it from the Play Market and, after launching, click on the appropriate button.
When Huawei enters eRecovery
Huawei smartphones can switch to eRecovery mode in the following cases:
- intentional entry for recovery;
- unintentional key presses;
- failure during the update or firmware procedure.
To restore data, you usually enter the eRecovery menu by simultaneously pressing and holding the volume and power keys for several seconds when the smartphone is turned off.
In most models, the volume button must be held in the increase position when turned on, but it happens the other way around. After the recovery menu appears, you must also move between menu items using the volume button.
Unintentional keystrokes often occur due to the user not knowing how to log into eRecovery. But it also happens that when assembling a Huawei smartphone, mistakes are made and one of the keys becomes jammed. In this case, the EMUI mode may appear randomly, although manufacturers have specifically made it difficult to enter using a combination of presses.
A failure to update the software or firmware of a Huawei smartphone can also cause it to enter eRecovery mode, since the device needs to somehow complete the process.
If the approach described above does not help achieve the desired effect, and the desired mode does not start on Honor, you should enter it in another way:
How to work in the recovery environment Recovery Mode
In the Recovery area, there is no graphical interface to which all owners of smartphones and tablets running Android OS are accustomed. And touch controls don't work there either. Therefore, it would be a good idea to consider how to use Android Data Recovery mode.
The main window of standard Recovery is a list of functions. Moving between menu items is done using the mechanical Volume Up/Volume Down keys, and selecting an item is done with the Power button.
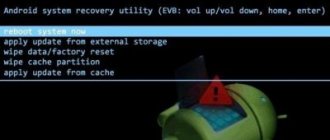
Once in stock Recovery Mode, the following tools will be available to you:
- Reboot system now. Used to reboot the mobile device and enter the Android GUI.
- Wipe data/factory reset. Clears the device's internal memory of installed applications, notes, contacts, etc. At the same time, personal photos, videos and documents will remain intact. This function allows you to get rid of various operating system failures.
- Wipe cache partition. Removes all information from the system cache. It is used when the installed software does not work correctly, as well as before flashing the gadget’s firmware.
- Backup and restore. Creates a system backup and restores the phone using previously created points.
- Mounts and storage. Allows you to clean one of the system partitions.
- Advanced. Opens additional Recovery capabilities (restarting this mode, erasing the dalvik cache, etc.).
You should work very carefully in the Recovery recovery environment, since all actions performed are irreversible and can lead not only to the permanent deletion of all user information, but also to turning Android into a “brick”.
How to enter the Recovery menu on Android on different devices
Hello. Do you know how to enter the Recovery menu on Android? If not, then this article is definitely for you. Now we will look at what ways exist for this and why it may be needed.
A little theory
To begin with, it is worth noting that Recovery is a specialized service of the Android operating system, which is available on all devices. You can use it to launch when you want to quickly delete all data in the gadget, restore to factory settings, change the firmware, etc.
If the Recovery has never changed, it is called stock, if the firmware has been changed, it has become custom. The factory service, which is installed on new devices, has somewhat reduced functionality, but even with its help you can reset system parameters or install cool firmware.
After updating Recovery, the user receives many new functions on his Android, for example, backup recovery, the ability to get root, creating backups and many other options.
Standard instructions
In order to enter the Recovery menu, you will need to turn off the device, then you need to hold down a special combination of buttons until the display is activated. In fact, there is no one traditional way by which you can access the desired service; each manufacturer’s phone has its own combination, but there are several almost universal options, they will be described below:
- The menu can be accessed through a computer; to do this, you need to connect it to your smartphone and send it to recovery mode via the Windows command line.
- It is easy to log in using developed third party applications.
- Thanks to the “Terminal”, in which the command is entered (it won’t work without root rights).
It is interesting that there is equipment that does not have Recovery, so you will need to download it yourself (if there is a custom service for this model). Use the volume keys to navigate through the items and select the desired section using the power/lock key.
There is another simple transition method. Unfortunately, not all models support it. On a functioning device, press ON/OFF for a while. The display will display a menu with different variations, where there should be a line “Go to recovery” or something similar. If all else fails, you will have to use a combination for a specific model to enter.
- Lenovo – you need to turn off the Lenovo device and immediately hold the Volume “+” and “turn on”. If nothing works, you can press power and rock the volume.
- Nexus – owners of Google Nexus devices need to first visit Fastboot mode, only after that they can go to the service menu. To do this, use the power key and the “Down” sound. Next, select “Recovery mode”.
More on the topic: How to earn bitcoins on Android?
- HTC – the combination of Volume Down and startup will save you; there are models that use volume switching with startup. On many HTC gadgets you get into the Bootloader, only then use the sound level buttons to go down to “Recovery” and enter it with the power button. It is worth noting that Bootloader also contains the “Factory reset” item; it resets all device values to factory settings.
- Samsung – on all new Samsung smartphones, a command has been created to enter the service: volume up + Home key + ON. For older models, a combination of “power” and “home” is used.
- Meizu – recovery mode cannot be found in these phones, but there is a menu from which you can download the firmware or reset system parameters. To activate, press “ON” + Volume “UP”.
- Xiaomi (Xiaomi, Xiaomi) – you will have to turn off the phone and press Volume Up + Power. Recovery on Android Haomi is available in several languages that can be changed.
- LG – you should hold the Volume and Power buttons until the company logo lights up. After that, release them, press again, and wait for the menu to load.
- Huawei, a Chinese device manufacturer, has made 2 options for calling the service: a button for changing the sound (+ or -) and turning it on.
- Sony Xperia – owners of a Sony Xperia gadget will need to turn off the device in order to enter recovery mode. After deactivating it, you need to turn it on again and wait for the indicator light or the logo to appear, after which the volume control is pressed. There are models that use clicking on the manufacturer's inscription. Another option is to turn off the smartphone, press Power and wait for vibration, release the button and press the volume control rocker.
- Motorola - controls are the same as on Nexus devices.
- Fly – hold until the manufacturer’s inscription or vibration of the volume (+/-) + on/off combination appears (depending on the model).
We use the software
As noted above, there are special applications that allow you to access the required service menu with one click. In order to start working with such a program for Android, you need to open the Play Market, find the appropriate product and download it. One of the most successful options is Quick ReBoot.
After you install and launch the application, select the Recovery section. The device will reboot to recovery mode and you can continue to work with the necessary parameters.
For example, you need to restore the factory settings on the tablet, therefore, you use the Wipe data item, to update the firmware, select the Apply update from section.
Using custom Recovery
The stock recovery mode has somewhat limited capabilities, which in some cases are simply not enough. So, you won’t be able to reflash your smartphone using it or install the required application from a memory card. Therefore, advanced users replace the standard Recovery with a custom one (CWM or TWRP), which is equipped with more advanced functionality.
As an example, let's look at the installation procedure and subsequent use of ClockWorkMod (CWM) Recovery:
The installation of Android CWM Data Recovery will begin. This process will not take much time. After it is completed, you can enter the custom recovery environment using the same keys that were used to load the stock Recovery.
In addition to the standard set of tools, the new resuscitation area will be supplemented with the following functions:
Having figured out how to work with the Recovery environment, you can flash smartphones or tablets, reset settings, create restore points and perform other specific actions without third-party help.
"(by Dreamer...) recovery was mentioned, but what it is and what can be done by replacing it with a custom one was not described in detail. Meanwhile, this is one of the most important components in fine-tuning the phone, which allows you to replace the firmware or make a backup copy of the current one. In this article I will try to correct this unfortunate omission.
How to exit Android recovery
How to exit recovery mode on Android. And since you already know how to use the Recovery menu, but you have a problem: how to exit this mode? Everything is very simple!
As you know, the recovery menu is a special boot mode for a smartphone, with which you can install updates, other firmware, connect to the device using a desktop PC, and much more. It happens that the user opens the Recovery menu accidentally. How does this happen? For example, in a bag, the smartphone reboots and when mechanical keys are pressed with other objects, the recovery menu can be loaded. How to get out of it?
The first option is to select Reboot or Reboot system now.
Press and in this case the smartphone will reboot, and it will boot in normal mode.
The second option is Power off or Power down. This item means turning off the smartphone, that is, after turning it off, it will not turn on on its own.
This is a standard recovery menu, which looks somewhat different on most smartphones. And remember that moving through it occurs using mechanical keys to decrease or increase the volume, and confirmation is usually carried out by pressing the on/off button. But there are other versions of recovery.
For example, TWRP is a menu that you can navigate by tapping on the screen. You need to select "Reboot" or Reboot depending on the language you are using.
The device will reboot normally. You can also select Power Off to turn off the smartphone.
Android and bootloader
For a more complete understanding of what Recovery is in general, in my opinion, it is also worth talking about what a bootloader is and how it is connected to all this. So, Bootloader is a bootloader - an application that is the very first to launch on your device, reads its configuration, and based on it, either loads the operating system (Android). Analogues on desktop OSes are MBR on Windows and Grub with LILO on Linux.
| Android Bootloader |
In addition to loading the OS, the bootloader provides the ability to select an OS to launch (if there are several of them), select the OS startup mode (for example, “Safe Mode in Windows”), and also launch auxiliary applications, which includes Recovery. In some cases, the bootloader always provides a menu for selecting OS\modes\applications, in others you need to press a certain key/key combination to display it, and in others there is no menu at all and alternatives to the main OS are launched by pressing keys and\or their combinations. On desktop OSes, the first two options are most common, on mobile operating systems, the last two are most common.
Simplified OS boot scheme
note. The Bootloader menu in Android is often mistakenly called the device BIOS. But this is wrong, because... The bootloader and BIOS are completely different things with completely different tasks.
What is Recovery
Recovery is an additional application for restoring\resetting\modifying\replacing the firmware\OS of a smartphone. The standard recovery of the vast majority of smartphones allows you to perform only the first two operations. Custom, i.e. non-standard, user-set recovery allows you to do much more. To install a custom recovery, as a rule, you need root privileges on your device (specifically, when installing from the device itself, without the participation of a computer) and, in some cases, a modification of the bootloader. Installation is carried out either using special applications in the market, or using a computer. It is also possible to launch custom recovery using a computer without installing it on the phone (via adb). Instructions for installing recovery may vary from phone to phone, so they will not be given here. They can be found without problems on the Internet and on the Russian forum 4pda and foreign xda-developers in particular, but in general, as a rule, it is enough to install a certain application from the market (more about them below) and use it to install recovery. As you can understand from the preceding section: Recovery and the firmware itself are not directly related to each other, therefore, modification of one of the components, in the standard situation, will not affect the other, which means that if you, say, screw up the current firmware of the device, it does not become “ brick” and can be easily restored by installing another one via Recovery.
“Standard” functions of custom recovery
- install
- mount
- allows you to mount/unmount various partitions. This is required in rare cases, usually when installing system modifications. You don’t need to touch it unless it’s explicitly stated on the page describing the component being installed, or the installation will not display an error stating that the required partition is not mounted (for example, something like “error... no mount /system”).
— installs firmware\kernel\system utilities (for example, a set of applications from Google for cyanogenmod) from a special file. Such files are ordinary zip archives with a certain structure. Some of these archives come with a special utility: Aroma Installer, which is essentially a graphical installer with the ability to select installation options. The presence/absence of Aroma Installer has nothing to do with the quality or popularity of the firmware/kernel/utility.
backup\restore
- perhaps one of the most important components - allows you to make a full or partial backup of your current system. It is EXTREMELY recommended to make full backups when changing one firmware to another, or one built on a different version of Android (for example, when upgrading from cyanogenmod 9 to 10) and partial backups (boot and system sections) in case of “minor” ones (i.e. within one versions, for example, from 10.1.1 to 10.1.2) firmware updates. Also, modern recovery generates an md5 sum for the backup archive, which allows you to control its integrity (no damage). You can disable it, but I don't recommend it. I would also recommend keeping at least 2 recent backups. If the last one gets damaged (I personally haven’t had this happen, but there is a possibility), we have the opportunity to recover from the penultimate one. The probability of damage to both backups is much lower than one (if you do not consider physical damage to the media where they are recorded).
wipe\format
— cleaning\formatting internal memory partitions. In general, formatting is not required in the vast majority of cases; usually a simple wipe is sufficient. It is recommended to reset the cache and dalvik-cache partitions when changing the firmware. Clearing the data partition (aka Factory Reset) leads to resetting all user settings, as well as applications installed by him, in other words, the firmware returns to its original state. The system partition stores the firmware itself and, as a rule, is automatically formatted when installing a new one.
Video instruction
Xiaomi has its own menu and in it, to reboot the smartphone in normal mode, you need to select the Reboot item.
Or Power off to turn it off.
In general, even if the recovery menu interface of your smartphone is different, you can exit it by selecting Reboot or Power off in the menu.
Friends! If our site helped you or just liked it, you can help us develop and move on. To do this you can:
- Leave a comment on the article.
- Subscribe to our YouTube channel .
- Subscribe to our VKontakte group .
CAHEK80 | from Redmi 5 Plus
| I rebooted my phone and accidentally got into recovery mode. I can’t get out of it in any way: I click Reboot - it returns to the same menu, Wipe data - the same thing. Attempts to turn off the device do not help - the same menu with three buttons appears every time. What to do? |
Karasev Evgeniy replied: 2020-01-22 16:03:55 Hello. First, tell the whole truth: what and how did you do it? You don’t get into that mode like that and get out very easily.
acidmist replied: 2020-01-22 16:12:11 Where do the complaints against me come from? What is the point of keeping silent about something if I want to solve the problem, and especially to whom will I hide “my actions”? If you can't help, it's better to pass by
If you can't help, it's better to pass by
1619716888 | from Redmi Note 5
CAHEK80 | from Redmi 5 Plus
Karasev Evgeniy Hello. First, tell the whole truth: what and how did you do it? You don’t get into that mode like that and get out very easily.
CAHEK80 replied: 2020-01-22 18:08:17 hello! You are right about the truth, that the author is not telling the truth. I had this happen, without booting into the system it was thrown into recovery. But this happened to me due to quick firmware changes and tests of different mods, after which I did not clean the tails. so it jammed. and again, you are right, after the author’s words and what he doesn’t say, there is no point in helping.
CAHEK80 | from Redmi 5 Plus
Karasev Evgeniy Hello. This is why I can think that everything is not so simple here. If the Redmi Note 5 device had crashed during the update (and it could have been installed overnight), it would have most likely happened when switching to Android 9 (that is, six months ago, not now, and even on a Chinese version with a patched bootloader).
If your Huawei phone returns to eRecovery mode after a reboot and you cannot exit it in the usual way, you should first check the assembly:
Modern custom Recovery
ClockWorkMod\ClockWorkMod Touch
| Perhaps the most famous custom Recovery, which is recommended in the vast majority of firmware instructions and is supported by almost all modern smartphone models. ClockWorkMod Touch, unlike the original, has a touch menu and is installed only in the paid version of RomManager. The big advantage of CWM Touch, compared to other touch recovery, is the ability to control physical buttons (volume and power buttons), which will allow, in case of problems with the sensor, to return the original firmware and return it under warranty without any problems (if, of course, you didn’t forget to reset something like the firmware counter in smartphones from Samsung). Among the additional options, we can note the possibility of creating an SD-Ext partition: roughly speaking, a piece is “bitten off” from the memory card into a separate partition, formatted in Ext2/3/4 (file system linux) and is attached to the main memory of the smartphone: which allows you to install more applications on those devices where the manufacturer did not take care of the internal memory. The partition size can be set from 128Mb to 4096Mb (4Gb). |
However, this recovery has one drawback - when creating a backup, it is impossible to choose what exactly to save (boot\system\data) - everything that requires additional time and space on the drive is saved. Also from my own experience: the CWR Touch on the SGS3 cannot install the CyanogenMod 10.1 update obtained using CyanDelta. A small hint: it is not necessary to install CWM Touch through the very expensive Rom Manager Premium - you can easily get by with cheaper (or even free) tools, like Mobile ODIN. You can download official recovery images in img format from the following link: https://www.clockworkmod.com/rommanager Other formats (for example tar for ODIN) can be found on xda-developers.
There is also a modified version of CWR Touch, which contains additional settings (design) and options (choose what to save in a backup copy) - in general, a very, very nice thing. It's called PhilZ Touch Recovery
, you can download it at xda-developers
Installed using the RomManager applicationDownload free version
Buy for ~186r
4EXT
| It is very reminiscent of ClockworkMod Recovery, so 4EXT can even be mistaken for a kind of add-on - it can do everything, plus a little more. It differs from CWR in supporting themes (both in text and touch modes) and some additional functions. By the way, Touch Recovery appeared with them much earlier than with CWR. Among the additional functions: the ability to connect a memory card as a drive from Recovery itself (quite convenient when experimenting with firmware), as well as convert Ext3 to Ext4 and vice versa (irrelevant for Android 4.x). Personally, I liked the touch mode much more than in CWR - the lines are wider, i.e. It's easier to navigate and there are icons to make navigation easier. |
There are some drawbacks: in touch mode there is no way to control the menu using physical buttons - i.e. If the sensor breaks down, restoring the original firmware will be much more difficult. And what else I didn’t particularly like was the rather small list of supported models. In general, if you often work with firmware and your smartphone model is supported by 4EXT, I recommend it. It costs less than CWR (Touch version) and is more convenient. And if the sensor breaks down, nothing prevents you from flashing a regular CWR using a computer and restoring the original firmware from it.
Installed using the 4EXT Recovery Control applicationBuy for ~93r
TWRP
| The youngest of all three Recovery. It only has a touch interface, but it also provides a separate view for tablets (see screenshots). The touch interface is self-sufficient and is not a kind of add-on over the text interface (like CWR and 4EXT), which in my opinion is more convenient. Particular attention is drawn to the element for confirming any operation - it is designed in the form of the famous “slide to unlock”. In general, using the TWRP interface is noticeably more convenient than that of its competitors. And I haven’t yet mentioned the changeable design themes, which can affect not only the appearance, but also the functional arrangement of elements. Among the functional differences is the ability to select partitions saved in the backup, and, in addition to the standard ones, you can add a backup copy like this - You can also add a cache and Recovery itself. I was also very pleased with the ability to immediately specify a name for the backup archive - very convenient. For example, I gave the original firmware the name “original”, which allows me to skip it when clearing backup copies of unnecessary ones without specifically looking for them among similar names. Repeating the words from teleshops, “but that’s not all” - the backup copy can be compressed (takes up less space, but at the same time it takes significantly longer to create) and disable the generation of MD5 sum (it is created faster, but if the archive is damaged, this will not be detected ). It is also worth mentioning that when creating a backup, TWRP immediately, even before starting, shows the amount of memory occupied by the partitions, as well as the free space on the drives. In general, when it comes to backup/restore, TWRP is head and shoulders above CWR and 4EXT, which is good news. Just like 4EXT, this Recovery allows you to mount a memory card like a drive to a computer without switching to the firmware. Moreover, this is done even on SGS3, where full-fledged firmware cannot, without special crutches, connect a flash drive as a regular drive, and not via MTP. What is also notable about this recovery is its support for technology full disk encryption (full disk encryption), which can protect your data if your phone is lost. However, it is quite possible to bypass it, so you still shouldn’t store any particularly valuable information on your smartphone, at least in open form. Nevertheless, this is a significant advantage of this recovery for those who care about the security of their data. TWRP on Smartphone | TWRP on Tablet |
In general, this recovery is perhaps the best that exists at the moment: convenient, functional, completely free. Highly recommend. I almost forgot - when creating an archive with a backup copy, this miracle of programming thought is capable of using several cores of your smartphone - which has a very positive effect on the speed of operation.
Installed using the GooManager application(MENU => Install OpenRecoveryScript)
Download free version