Good afternoon. For those who are not yet aware, Xiaomi began to block the bootloader quite a long time ago. This is due to the fact that the company has entered the international market, and for certification from Google and the use of Gapps, there are some nuances regarding the security of the device. The further into the forest, the thicker the partisans are, and the same thing happens here. Previously, you could flash a phone with any firmware in three steps, but now you have to tinker with the Deep Flash Cable. But first, let's find out if it's blocked for you or if you're lucky with the old firmware.
- A newer method is through the “For Developers” menu
- Old method via fastboot (does not work on MTK processors)
What is Bootloader
A bootloader is a special program that runs every time you turn on or reboot your smartphone and checks the installed operating system for errors and then launches it. Bootloader also protects user files and OS components from outside interference.
Most manufacturers, including Xiaomi, lock the bootloader, protecting it from changes. In terms of security, this is good, but blocking deprives users of the ability to fully control their gadget.
An unlocked bootloader allows you to install a custom recovery, get root rights, or flash a custom build of the OS. It is for installing unofficial firmware that it is usually unlocked.
Unlocking Bootloader deprives the smartphone of OTA updates. In addition, services such as Google Pay refuse to work on smartphones with an unlocked Bootloader.
In most cases, the Mi Flash Unlock program is used to unlock the Xiaomi bootloader. It allows you to log into your Mi account, send an unlock request and carry out the procedure using a PC and a USB cable.
What is reboot to bootloader on Android
This is a command or in other words a function that puts the Android device into bootloader mode. The option is found in the recovery console – recovery. In some tool applications, you can boot into the bootloader by holding down a specific combination of buttons, which varies from manufacturer to manufacturer.
You can also switch your smartphone to bootloader mode in fastboot. Simply enter the command fastboot reboot-bootloader, and the smartphone or tablet will switch to the specified mode.
Official and unofficial unlocking method
There are two ways to unlock Bootloader:
- Official - works fine on all smartphones.
- Unofficial unlocking requires special skills, there is a high chance of turning the phone into a “brick”.
The official way is to link your Mi account to your phone and unlock it using the Mi Flash Unlock program. However, from the moment you apply to unlock the Xiaomi bootloader (sent a request to the server), at least 360 hours . Only after this the account will receive permission to unlock. In some cases, the maximum possible time of 720 hours is assigned.
It is also worth noting that if the phone and account have been used little, Xiaomi may refuse to unlock and advise the user to use the phone more often. In this case, the unlocking process must be repeated after a few weeks.
Unofficial unlocking allows you to unlock the Xiaomi bootloader without an account and requires a modified version of the Mi Flash Unlock program for a specific phone model. You will also need to install all ADB and Fastboot drivers for subsequent work with the command line.
Many phones, in case of unofficial unlocking, are flashed using contact closure (the so-called EDL mode). This is strictly not recommended. Even in workshops. The risk of getting a “brick” is extremely high.
Attention! An unlocked bootloader allows hackers to access the device even remotely. Therefore, after carrying out all the actions, it must be blocked again.
Both options require a computer with ADB drivers and software installed. It is impossible to unlock Xiaomi bootloader without a PC. On a phone without a PC, you can only check the status of the bootloader: open or closed.
Below is the official Xiaomi bootloader unlock procedure for Redmi, Mi and POCO.
Unlocking the bootloader
To allow unlocking the OS bootloader, you need to go through 2 steps:
- Link your smartphone to your Mi account.
- Unlock Bootloader.
The first stage is preparatory and consists of linking the smartphone to the Mi account (if this has not been done). This action is required. Skip it if your phone is already linked to a Mi account.
Attention! During unlocking, all user files and applications will be deleted. The smartphone will be reset to factory settings. Therefore, before performing the unlocking procedure, it is recommended to backup your data.
Linking your phone to your Mi account
If your phone is linked to a Mi account, proceed to the next step - working with the Mi Flash Unlock program.
- Log out of your account. This is a necessary step, otherwise the system will not be able to check the phone and link it.
- Switch from Wi-Fi to mobile Internet.
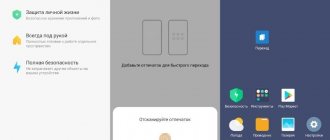
- Go to the "About Phone" section.
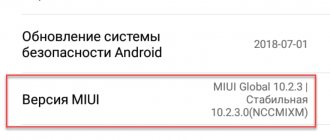
- Click on the “MIUI Version” line 7 times to activate the developer settings.
- Return to the main settings menu and find “Advanced settings.”
- Tap on the “For Developers” item.
- Tap "Mi Unlock Status".
- Confirm your actions by agreeing to the warning that appears.
- Select "Link account to device."
- MIUI will require you to log in to your account. Sign in.
The binding process will begin, which will not take much time. You will see the appropriate message when it is completed.
Wait until the required 360 or 720 hours have passed. You can check how much time is left before unlocking by going to “Mi Unlock Status” - the third screenshot above.
As soon as official permission is received, we move on to the second stage with the Mi Flash Unlock program.
Unlocking using Mi Flash Unlock
Step-by-step instructions on how to quickly unlock Xiaomi bootloader:
- Enable developer mode: to do this, go to settings, go to the “About phone” section and tap the MIUI version column 7 times.
- Then return to the list of options, select “Advanced settings”, go to the “Developer options” section and move the slider next to “USB debugging”.
- Launch the Mi Flash Unlock program to unlock the bootloader on your PC, enter your Mi account username and password, and then click “Login.”
- The unlock permission check will begin. Turn off your smartphone completely and start Fastboot mode (by holding down the power and volume down buttons).
- Connect your phone to your PC via cable and click the “Unlock” button in the Mi Flash Unlock program window. Once your smartphone is connected, it will become active.
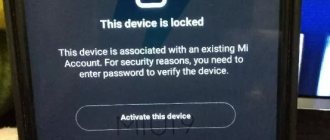
Pay attention to what happens after the operation (second screenshot).
During unlocking, the smartphone will reboot. You will be taken directly to the operating system. After unlocking Bootloader, you can begin installing a custom recovery, obtaining root rights, or installing alternative firmware.
TOP 5 productive Xiaomi smartphones according to AnTuTu rating:
- 1 Black Shark 4 Pro
867578 points - 2
POCO F3 Pro821847 points
- 3
Mi 11 Ultra817225 points
- 4
Mi Mix Fold815000 points
- 5
Mi 11 Pro804210 points
Recovery, Edify and Aroma Installer
Having detected the volume up key held down, aboot does almost the same as during a normal boot, but uses the recovery partition instead of boot. The partitions are identical in format and often contain the same kernel, but the contents of the RAM disk are significantly different. If in the case of the boot partition the purpose of the RAM disk is to create the initial conditions for further booting the system, then recovery is a mini-OS that can work separately.
Stock recovery is very simple. All that its RAM disk contains is the executable file /sbin/recovery and (not always) a set of background images in the /res directory or any other directory. When booting, the Linux kernel runs /sbin/recovery, which displays a simple menu that allows you to install firmware signed with the manufacturer's digital key or perform a factory reset.
Custom recovery is much more complicated. This is no longer just a menu with a background image, but an entire operating system capable of installing any firmware, making backups, formatting partitions and much more. Modern versions of TWRP generally support control using a touch interface, replaceable skins that completely change the appearance of recovery, a login password and a terminal emulator along with an on-screen keyboard. Plus, custom recoveries include BusyBox (a set of Linux command line utilities) and an ADB server running with root rights. So recovery mode is very convenient to use for debugging and operations such as, say, dumping partitions. For example, the boot section (example for Qualcomm chips):
$ adb shell dd if=/dev/block/platform/msm_sdcc.1/by-name/boot of=/sdcard/boot.img
But the main task of recovery is, of course, installing firmware. More precisely, it would be the main task if recovery had such a function. In fact, all recovery does when you click "Install ZIP..." and select the firmware is unpack the ZIP file (usually into the cache partition) and run the /META-INF/com/google/android/update-binary file inside him. It is update-binary that installs the firmware, following the instructions from the updater-script file (it lies nearby).
The instructions themselves are written in the Edify language, which includes a set of commands that may be needed during installation: mount, unmount, package_extract_file, symlink, run_program and others. We will not discuss all these commands here, they are quite simple, and to familiarize yourself with them, just unpack any firmware and open updater-script in a text editor. Let me just say that usually such files are generated automatically when building a system from source, and only authors of highly specialized firmware (containing only the kernel, for example) write them themselves.
Updater-script fragment from CyanogenMod 12.1
Recovery does not impose any restrictions on the update-binary file - the main thing is that it can be launched. This gives manufacturers the opportunity to use any application that can run on top of the Linux kernel instead. It is not at all necessary that it install the firmware at all. As part of the Aroma Installer project, an update-binary option is being developed, which allows creators of custom firmware to implement a graphical installer with a choice of various installation options and options.
The author of Aroma Installer also created Aroma Filemanager - a full-fledged file manager with a built-in terminal emulator. To launch it, you need to reboot into recovery and flash the ZIP file. Naturally, no firmware will be installed, because update-binary inside the ZIP file is only a file manager, it does not perform any installation operations.
Terminal emulator built into Aroma Filemanager
The "dummy" update-binary is often used to distribute various kinds of scripts. It's much easier to rename a script to update-binary, package it in a ZIP file, and have someone flash it than to explain how to run scripts using ADB. This is exactly what osm0sis did with his script for unlocking the bootloader of Nexus devices. If you download its ZIP file and look inside, you will find updater-binary, inside of which is a regular sh script.
Xiaomi firmware without bootloader unlocking
If the Bootloader is locked, then there is only one way to flash Xiaomi with a locked bootloader - install stock MIUI using the official Mi Flash Pro program. Installing a custom system will not work this way.
Step-by-step instructions for flashing firmware without unlocking the bootloader:
- unzip to any location on your PC.
- Launch Mi Flash Pro, go to the Mi Flash tab.
- When you launch it for the first time, the program will prompt you to install the necessary drivers. Click the Install button.
- After installing the drivers, click on the Select button and in the Explorer window, select the folder with the unpacked firmware.
- Turn off your smartphone and then hold down the Power and Volume Down buttons at the same time to enter Fastboot mode.
- Connect your smartphone to your computer using a USB cable.
- In the program window, click Refresh.
- At the bottom of the window, check the clean all and lock option and click on the Flash button.
The firmware will begin, which takes 5–10 minutes. After its completion, Bootloader will remain locked. You will be able to use OTA updates, there will be no problems with contactless payment and other Google services.
Flashing Xiaomi firmware via Fastboot with a locked bootloader is only possible in this way. All user data will be deleted.
How to find out whether the bootloader on Xiaomi is unlocked or not?
Now I will tell you about 3 ways to check the bootloader status on Xiaomi and Redmi smartphones. I recommend checking using at least 2 methods, since there are still models (purchased for “very cheap” or used) that were flashed or hacked to bypass unlocking the bootloader. In this case, the first method may show a line that the bootloader is unlocked, but when checking through ADB, everything will be different ( only the PC will show the truth ).
METHOD 1: through the phone menu
The easiest way, built into your device and does not require additional programs.
- Open the standard “Settings” of the smartphone;
- Go to the “About phone” item;
- Now click on the line “MIUI Version” 5 times, the message “ You have successfully become a developer ” will appear.
- We return to the main menu and find the “Advanced settings” item, click on it.
- We look for the “For Developers” item and go to it.
- Now you need to find the line “ Mi Unlock Status ”. When you first log in, you must give permission and agree to the warning.
- If the bootloader is locked, at the very top there will be a corresponding message “Bootloader locked, device protected.” If the bootloader is unlocked, the message “Bootloader unlocked” will appear on the entire screen.
METHOD 2: via computer
If for some reason the first option does not suit you, you can check whether the bootloader on Xiaomi is unlocked using a PC. Instructions are included for two operating systems - Windows and Linux .
Windows
This is a difficult method, but it is the most accurate.
ADB.zip
- Download the archive with ADB files and unpack it to the root of the system drive C, so that the path is “ C:/adb/ ”.
- Turn off the smartphone and put it into fastboot mode. To do this, simultaneously press the power and volume down keys.
- Connect the device to the computer using a USB cable.
- On your PC keyboard, press “Win” + “r” . The Run window opens.
- Type “cmd” and click “OK”. The system command prompt appears.
- In the command line, write the command “cd c:/adb” and press Enter.
- Now we enter the command “fastboot oem device-info” and we see the inscription we need.
If “true” is specified, the bootloader is unlocked, otherwise “false”, which indicates a locked bootloader.
Linux
- Download the ADB files from the link above and transfer them to the desired folder.
- Open a terminal and write the following command “adb - sudo apt-get install android-tools-adb android-tools-fastboot”.
- We switch the smartphone to fastboot mode, as in the above option. The entered inscription is disconnected, and next to each part of the text we see the necessary information about the bootloader:
sudo fastboot devices – the device number appears here, sometimes the model is added;
sudo fastboot oem device-info – and here is the status of the bootloader, similar to that on the Windows operating system.
If the message “ waiting device ” appears, most likely the actions were not performed as an administrator.
METHOD 3: when you turn on the device
And the last, third way to check the status of the bootloader is to turn on the phone, or rather its boot screen. To do this you need:
- Turn off your Xiaomi, wait about 20 seconds for all internal processes to completely stop.
- Turn on the phone again (press and hold the power button).
- If, during booting, “Unlocked” is written the bottom/top
How to lock the bootloader
There are two ways to lock Xiaomi bootloader. We looked at the first one above - this is standard firmware using the Mi Flash Pro program with the clean all and lock . We will not consider this option again.
The second method is based on working with the Windows console or the PowerShell command line. It is more complex, but does not require a complete firmware change.
This unlocking method uses ADB drivers and is not suitable for Xiaomi smartphones released before 2021. If you have just such a phone, you will have to use the first option with full firmware.
First, you will need to install all ADB drivers for your smartphone on your PC.
- With your phone turned off, press the power and volume down buttons to enter Fastboot.
- Connect your smartphone to your PC using a USB cable.
- On your computer, go to the directory with the ADB and Fastboot drivers installed.
- Right-click while holding down the Shift key on an empty space in the folder and select “Open PowerShell window here” from the menu that appears.
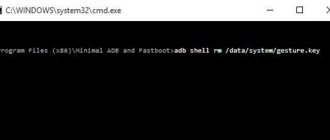
- In the console, write fastboot devices and press Enter. The console will show the status of the bootloader.
- Type fastboot oem lock and press Enter. This is the command to lock the bootloader. If everything is fine, OKAY will appear in the console.
- Reboot using the fastboot reboot .
This blocking option in some cases allows you to save user data. The chance that all files will be deleted is approximately 50%. However, during the firmware they will be removed with a 100% guarantee.
Benefits of an unlocked bootloader
An unlocked bootloader opens up exactly the same possibilities for the user as on a PC, namely:
- Flash any operating system (available for your device).
- Installation of individual modules, OS kernels, applications, patches.
- Freely migrate between stock firmwares, especially if they are based on different versions of Android.
- Easily create backup copies of the current OS and/or applications, as well as restore them without using a PC.
- Use Dual-Boot and install two or more operating systems, both in internal memory and on an external SD card.
- Wider recovery options in case of unsuccessful firmware.
And this is not the entire list of possibilities after factory unlocking Android.
If the phone does not boot after unlocking the bootloader
If, after unlocking the bootloader, you experience a bootloop (endless loading) and your Xiaomi phone does not boot beyond the logo, the situation can be corrected in several ways.
The first is to flash the phone according to the standard scheme via Fastboot using Mi Flash Pro. We talked about this option earlier in the article.
The second method is to install a custom TWRP recovery. After this, you can roll out custom firmware or reset the phone to factory settings.
First you need to download the script for automatic installation of TWRP (look on the same w3bsit3-dns.com) and the firmware itself. The process is divided into several stages.
Stage 1: installing custom recovery
- Turn off the phone and start fastboot mode (by holding down the power and volume down buttons).
- Go to the folder with the downloaded recovery installation script and double-click on the “TWRP-Installer.bat” file.
- Select the appropriate recovery edition and press the appropriate button (for example, 1), confirm the action with the Enter button.
Once the installation process is complete, the phone will reboot into recovery. You can start working with it.
If you have a Xiaomi Mi A series, then after installing the recovery, immediately flash Magisk to obtain root rights. Otherwise the phone will not start.
Stage 2: Factory reset
- Turn off your phone, then hold down the Power and Volume Up buttons.
- In the main menu, go to the “Cleaning” section.
- Tap the “Selective Cleaning” button.
- Check all the boxes except Vendor , OTG and SD card .
- Confirm the action by moving the slider to the right.
- When the process is complete, click on the “Reboot to OS” button.
After completing these steps, the phone should boot into the OS. If this does not happen, then only full firmware of the device will help.
Stage 3: installing custom firmware
- Turn off the phone and go into recovery in the standard way (by holding down the power and volume up buttons).
- Go to the “Cleaning” section and move the slider to the right to perform it.
- Return to the main menu and select Install.
- Click on the "Select Drive" button at the bottom of the screen.
- Check the Micro SD Card item and tap OK.
- Find the downloaded ZIP file and click on it.
- Move the slider to the right to confirm the action.
- Click on the “Clear Dalvik/cache” button.
- Install Google services in the same way (if required).
- Click on the “Reboot to OS” button.
The first boot after the firmware can take from 5 to 15 minutes. You need to be patient. Next, you'll need to set up your phone. Unfortunately, user files will not be saved in this case.
Possible mistakes
During unlocking the Xiaomi bootloader, various errors may occur. Below are common errors and their solutions:
- Current account is not bound to this device indicates that this account is not bound to this device. You must first link your phone to your account, and then repeat the unlocking procedure.
- Your device isn't supported by Mi Unlock says that the phone is not supported by a specific version of Mi Flash Unlock. You probably have Chinese firmware or a custom version. You need to flash it to Global Stable and then repeat the procedure.
- Unknown error 90000 occurs if 5 devices have already been unlocked on the PC. The program will not allow you to carry out the same procedure with 6. You need to change your PC or operating system.
- Error 501 - ADB drivers need to be reinstalled. They are the ones that cause an error with this code. After reinstallation, restart your PC and start again.
- Network Error - network error. Try turning the VPN on/off and repeating the procedure. If this does not help, then the problem is on the Xiaomi servers. You just need to wait.
- Mi Unlock not connected to the phone - to solve this error, you need to move the Mi Flash Unlock program to the root of the disk. And make sure that there are no Cyrillic characters in the path to the EXE file.
- Unlock failed return to fastboot says that unlocking failed. Reinstall the drivers, turn the VPN on/off and repeat the procedure. If all else fails, try replacing the USB cable.
An unlocked bootloader gives users freedom of action. But at the same time, it negatively affects security and does not allow you to receive the necessary updates. So there is no need to unlock Bootloader unless absolutely necessary.